LncRNA PKMYT1AR promotes cancer stem cell maintenance in non-small cell lung cancer via activating Wnt signaling pathway
- PMID: 34856993
- PMCID: PMC8638142
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-021-01469-6
"V体育官网入口" LncRNA PKMYT1AR promotes cancer stem cell maintenance in non-small cell lung cancer via activating Wnt signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of human lung cancers, which has diverse pathological features VSports手机版. Although many signaling pathways and therapeutic targets have been defined to play important roles in NSCLC, limiting efficacies have been achieved. .
Methods: Bioinformatics methods were used to identify differential long non-coding RNA expression in NSCLC. Real-time RT-PCR experiments were used to examine the expression pattern of lncRNA PKMYT1AR, miR-485-5p. Both in vitro and in vivo functional assays were performed to investigate the functional role of PKMYT1AR/miR-485-5p/PKMYT1 axis on regulating cell proliferation, migration and tumor growth. Dual luciferase reporter assay, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), immunoblot, co-immunoprecipitation experiments were used to verify the molecular mechanism V体育安卓版. .
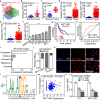
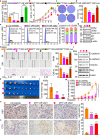
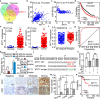
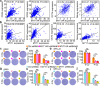
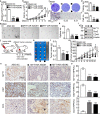
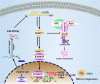
Result: Here, we identify a human-specific long non-coding RNA (lncRNA, ENST00000595422), termed PKMYT1AR (PKMYT1 associated lncRNA), that is induced in NSCLC by Yin Yang 1 (YY1) factor, especially in cancerous cell lines (H358, H1975, H1299, H1650, A549 and SPC-A1) compared to that in normal human bronchial epithelium cell line (BEAS-2B). We show that PKMYT1AR high expression correlates with worse clinical outcome, and knockdown of PKMYT1AR inhibits tumor cell proliferation, migration and xenograft tumor formation abilities. Bioinformatic analysis and a luciferase assay demonstrate that PKMYT1AR directly interacts with miR-485-5p to attenuate the inhibitory role on its downstream oncogenic factor PKMYT1 (the protein kinase, membrane-associated tyrosine/threonine 1) in NSCLC. Furthermore, we uncover that miR-485-5p is downregulated in both cancerous cell lines and peripheral blood serum isolated from NSCLC patients compared to reciprocal control groups. Consistently, forced expression of miR-485-5p inhibits the proliferation and migration abilities of tumor cells V体育ios版. Moreover, we provide evidence showing that PKMYT1AR targeting antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) dramatically inhibit tumor growth in vivo. Mechanistic study shows that PKMYT1AR/ miR-485-5p /PKMYT1 axis promotes cancer stem cells (CSCs) maintenance in NSCLC via inhibiting β-TrCP1 mediated ubiquitin degradation of β-catenin proteins, which in turn causes enhanced tumorigenesis. .
Conclusions: Our findings reveal the critical role of PKMYT1AR/miR-485-5p /PKMYT1 axis during NSCLC progression, which could be used as novel therapeutic targets in the future VSports最新版本. .
Keywords: Cancer stem cells (CSCs); Non-small cell lung cancer; PKMYT1; PKMYT1AR; miR-485-5p. V体育平台登录.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG, Yatabe Y, Austin JHM, Beasley MB, Chirieac LR, Dacic S, Duhig E, Flieder DB, et al. The 2015 World Health Organization classification of lung tumors: impact of genetic, clinical and radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10:1243–1260. - PubMed
-
- Lo Russo G, Imbimbo M, Garassino MC. Is the chemotherapy era in advanced non-small cell lung cancer really over? Maybe not yet. Tumori. 2016;2016:223–225. - PubMed
-
- Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R, Jemal A. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:271–289. - PubMed
-
- Roth A, Diederichs S. Long noncoding RNAs in lung cancer. Long non-coding Rnas in human disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016;394:57–110. - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
MeSH terms
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical (VSports app下载)

