Transthyretin and Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Product's Differential Levels Associated with the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 34737606
- PMCID: PMC8560178
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S327736
Transthyretin and Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Product's Differential Levels Associated with the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis (V体育2025版)
Abstract
Objective: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune, inflammatory joint disease VSports手机版. The identification of multifaceted etiological changes at the protein level in RA remains an important need. We aimed to identify differential proteins (DPs) and gene profiles to uncover inflammatory indicators and their association to RA pathogenesis. .
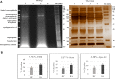
Methods: 2-DE and SWATH-MS were used to identify DPs in RA and healthy control plasma. Fluorescence phenylboronate gel electrophoresis (Flu-PAGE) with mass spectrometry was used for protein glycation in RA plasma. Disease specificity of identified DPs was confirmed by ELISA and Western blot analysis V体育安卓版. The gene expressions of selected DPs were evaluated by qRT-PCR in PBMCs of RA, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), spondyloarthritis (SpA), and osteoarthritis (OA). The functional implication of glycated protein was determined by in- silico and validated by in vitro analysis in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. .
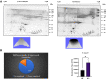
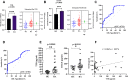
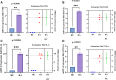
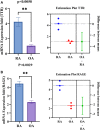
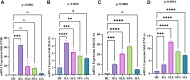
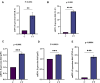
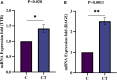
Results: A total of 150 DPs (127 increased and 23 decreased) were identified by 2-DE and SWATH-MS analysis in RA plasma compared to healthy control (HC). Nine proteins were identified as glycated by Flu-PAGE LC-MS/MS. Transthyretin (TTR), serotransferrin, and apolipoprotein-A1 (Apo-A1) were found to be differential and glycated. ELISA and Western blot results revealed the disease-specific increased expression of TTR and RAGE in RA. The qRT-PCR results signify the aberrant gene expression of TTR and RAGE, found to be associated with RA when compared with SLE, SpA, and OA PBMCs. TTR-RAGE interactions were predicted by in-silico and validated by in- vitro analysis using RA-FLS V体育ios版. The increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, and differently expressed TTR and RAGE were confirmed in fibroblast-like synoviocytes under inflammatory conditions. .
Conclusion: Our findings showed that the level of TTR was increased in RA plasma, along with an altered glycation rate. TTR and RAGE aberrant gene expression in PBMCs are the key events associated with RA, and TNF-α activates the NF-KB pathways and promote TTR and RAGE differential expressions that may have pathogenic/inflammatory significance. VSports最新版本.
Keywords: advanced glycation end products; differential proteins; post-translational modifications; receptor for advanced glycation end products; rheumatoid arthritis; transthyretin. V体育平台登录.
© 2021 Monu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
"VSports" Figures


References
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18001. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Rheumatoid arthritis; 2018. Available from: www.who.int/chp/topics/rheumatic/en/. Accessed October 8, 2021.
-
- Guo Q, Wang Y, Xu D, Nossent J, Pavlos NJ, Xu J. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018;6:15. - V体育官网入口 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zavala-Cerna MG, Martínez-García EA, Torres-Bugarín O, et al. The clinical significance of posttranslational modification of autoantigens. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol. 2014;47:73–90. - PubMed
V体育2025版 - LinkOut - more resources
VSports手机版 - Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous (V体育ios版)

