Inflammation-related pyroptosis, a novel programmed cell death pathway, and its crosstalk with immune therapy in cancer treatment
- PMID: 34522213
- PMCID: PMC8419056
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.62521
"V体育2025版" Inflammation-related pyroptosis, a novel programmed cell death pathway, and its crosstalk with immune therapy in cancer treatment
"V体育安卓版" Abstract
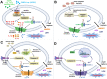
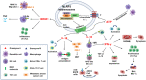
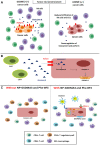
In recent decades, chemotherapies targeting apoptosis have emerged and demonstrated remarkable achievements. However, emerging evidence has shown that chemoresistance is mediated by impairing or bypassing apoptotic cell death. Several novel types of programmed cell death, such as ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis, have recently been reported to play significant roles in the modulation of cancer progression and are considered a promising strategy for cancer treatment. Thus, the switch between apoptosis and pyroptosis is also discussed. Cancer immunotherapy has gained increasing attention due to breakthroughs in immune checkpoint inhibitors; moreover, ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis are highly correlated with the modulation of immunity in the tumor microenvironment VSports手机版. Compared with necroptosis and ferroptosis, pyroptosis is the primary mechanism for host defense and is crucial for bridging innate and adaptive immunity. Furthermore, recent evidence has demonstrated that pyroptosis exerts benefits on cancer immunotherapies, including immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy (CAR-T). Hence, in this review, we elucidate the role of pyroptosis in cancer progression and the modulation of immunity. We also summarize the potential small molecules and nanomaterials that target pyroptotic cell death mechanisms and their therapeutic effects on cancer. .
Keywords: Nonapoptotic programmed cell death; cell death switch; immunotherapy; inflammasome; pyroptosis. V体育安卓版.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement (V体育官网入口)
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Reed JC. Mechanisms of apoptosis avoidance in cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 1999;11(1):68–75. - "V体育ios版" PubMed
-
- Mortezaee K, Salehi E, Mirtavoos-Mahyari H, Motevaseli E, Najafi M, Farhood B. et al. Mechanisms of apoptosis modulation by curcumin: Implications for cancer therapy. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(8):12537–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
VSports app下载 - Medical

