Efficacy of VSports app下载 - Lactobacillus fermentum Isolated from the Vagina of a Healthy Woman against Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Infections In Vivo
- PMID: 34489374
- PMCID: "VSports注册入口" PMC9705860
- DOI: 10.4014/jmb.2103.03014
Efficacy of Lactobacillus fermentum Isolated from the Vagina of a Healthy Woman against Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Infections In Vivo
Abstract
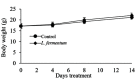
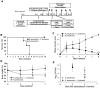
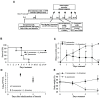
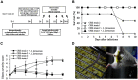
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) that produce Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase are increasingly reported worldwide and have become more and more resistant to nearly all antibiotics during the past decade. The emergence of K. pneumoniae strains with decreased susceptibility to carbapenems, which are used as a last resort treatment option, is a significant threat to hospitalized patients worldwide as K. pneumoniae infection is responsible for a high mortality rate in the elderly and immunodeficient individuals. This study used Lactobacillus fermentum as a candidate probiotic for treating CRE-related infections and investigated its effectiveness. We treated mice with L. fermentum originating from the vaginal fluid of a healthy Korean woman and evaluated the Lactobacilli's efficacy in preventive, treatment, non-establishment, and colonization mouse model experiments. Compared to the control, pre-treatment with L. fermentum significantly reduced body weight loss in the mouse models, and all mice survived until the end of the study. The oral administration of L. fermentum after carbapenemresistant Klebsiella (CRK) infection decreased mortality and illness severity during a 2-week observation period and showed that it affects other strains of CRK bacteria. Also, the number of Klebsiella bacteria was decreased to below 5. 5 log10 CFU/ml following oral administration of L VSports手机版. fermentum in the colonization model. These findings demonstrate L. fermentum's antibacterial activity and its potential to treat CRE infection in the future. .
Keywords: Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae; Lactobacillus fermentum; carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella; mortality; mouse model. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Aoudia N, Rieu A, Briandet R, Deschamps J, Chluba J, Jego G, et al. Biofilms of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus fermentum: Effect on stress responses, antagonistic effects on pathogen growth and immunomodulatory properties. Food Microbiol. 2016;53:51–59. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2015.04.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sanders ME, Gibson G, Gill HS, Guarner F. Probiotics: their potential to impact human health. Council Agric. Sci. Technol. Issue Paper. 2007;36:1–20.
-
- Salminen S, Gueimonde M. Human studies on probiotics: what is scientifically proven. J. Food Sci. 2004;69:M137–M140. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2004.tb10723.x. - DOI
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育2025版" Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

