IFN-λ therapy prevents severe gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease
- PMID: 34436524
- PMCID: PMC8667051
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2020006375
"VSports" IFN-λ therapy prevents severe gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease
Abstract
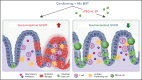
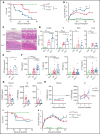
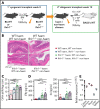
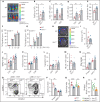
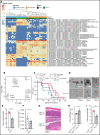
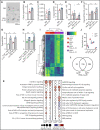
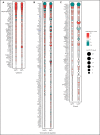
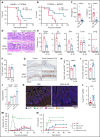
Immunopathology and intestinal stem cell (ISC) loss in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract is the prima facie manifestation of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and is responsible for significant mortality after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT) VSports手机版. Approaches to prevent GVHD to date focus on immune suppression. Here, we identify interferon-λ (IFN-λ; interleukin-28 [IL-28]/IL-29) as a key protector of GI GVHD immunopathology, notably within the ISC compartment. Ifnlr1-/- mice displayed exaggerated GI GVHD and mortality independent of Paneth cells and alterations to the microbiome. Ifnlr1-/- intestinal organoid growth was significantly impaired, and targeted Ifnlr1 deficiency exhibited effects intrinsic to recipient Lgr5+ ISCs and natural killer cells. PEGylated recombinant IL-29 (PEG-rIL-29) treatment of naive mice enhanced Lgr5+ ISC numbers and organoid growth independent of both IL-22 and type I IFN and modulated proliferative and apoptosis gene sets in Lgr5+ ISCs. PEG-rIL-29 treatment improved survival, reduced GVHD severity, and enhanced epithelial proliferation and ISC-derived organoid growth after BMT. The preservation of ISC numbers in response to PEG-rIL-29 after BMT occurred both in the presence and absence of IFN-λ-signaling in recipient natural killer cells. IFN-λ is therefore an attractive and rapidly testable approach to prevent ISC loss and immunopathology during GVHD. .
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology. V体育安卓版.
"VSports手机版" Figures
"VSports手机版" Comment in
-
"VSports手机版" IFN-λ: paving the road toward tissue protection in GVHD.Blood. 2021 Aug 26;138(8):596-597. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021012348. Blood. 2021. PMID: 34436528 No abstract available.
-
Henden AS, Koyama M, Robb RJ, et al. IFN-λ therapy prevents severe gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2021;138(8):722-737.Blood. 2022 Jun 2;139(22):3346-3351. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021014216. Blood. 2022. PMID: 35653165 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jenq RR, Ubeda C, Taur Y, et al. . Regulation of intestinal inflammation by microbiota following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Exp Med. 2012;209(5):903-911. - PMC (V体育平台登录) - PubMed
-
- Zeiser R, Socié G, Blazar BR.. Pathogenesis of acute graft-versus-host disease: from intestinal microbiota alterations to donor T cell activation. Br J Haematol. 2016;175(2):191-207. - "VSports app下载" PubMed
-
- Simms-Waldrip TR, Sunkersett G, Coughlin LA, et al. . Antibiotic-induced depletion of anti-inflammatory Clostridia is associated with the development of graft-versus-host disease in pediatric stem cell transplantation patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017;23(5):820-829. - PubMed
-
- Burman AC, Banovic T, Kuns RD, et al. . IFNgamma differentially controls the development of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome and GVHD of the gastrointestinal tract. Blood. 2007;110(3):1064-1072. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
VSports app下载 - MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
Substances
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
"VSports最新版本" Molecular Biology Databases

