V体育官网入口 - Sulfasalazine, a potent suppressor of gastric cancer proliferation and metastasis by inhibition of xCT: Conventional drug in new use
- PMID: 33988296
- PMCID: PMC8184680
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16548
Sulfasalazine, a potent suppressor of gastric cancer proliferation and metastasis by inhibition of xCT: Conventional drug in new use
Abstract
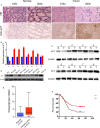
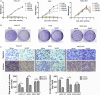
The aim of this study was to explore the role of sulfasalazine on proliferation and metastasis in gastric cancer by inhibition of xCT. The relationships between clinical characteristics and xCT expression were analysed. An immunohistochemical staining assay and Western blot were performed among gastric cancers and normal gastric tissues. qPCR and Western blot were also used to evaluate the mRNA and protein expression in the normal gastric cell and eight gastric cancer cells, respectively. CCK-8 and colony formation assays were used to evaluate the effect of sulfasalazine on the proliferation and colony formation ability of three gastric cancers. The effect of sulfasalazine on the migration and invasion abilities of three cancer cells was assessed by the Transwell assay. xCT protein is up-regulated in gastric cancer specimens and cells VSports手机版. Three gastric cancer cells with high, medium and low expression of xCT were selected for the following analyses. CCK-8 assays revealed that sulfasalazine could attenuate the proliferation of HGC-27 and AGS. Also, the colony formation assay revealed that sulfasalazine might attenuate the colony formation ability in HGC-27 and AGS cells. Plus, the Transwell assays demonstrated that sulfasalazine might attenuate the migration and invasion abilities in HGC-27 and AGS cells. In conclusion, higher expression of xCT is associated with advanced tumour stage and poor overall survival of gastric cancer. Sulfasalazine can attenuate the proliferation, colony formation, metastasis and invasion of gastric cancer in vitro. Further study is required to validate our findings. .
Keywords: gastric cancer; growth; metastasis; sulfasalazine; xCT. V体育安卓版.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd. V体育ios版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
"V体育平台登录" References
VSports最新版本 - Publication types
MeSH terms (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Substances
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
VSports最新版本 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (VSports)
Other Literature Sources
"VSports" Medical

