Donor Treg expansion by liposomal α-galactosylceramide modulates Tfh cells and prevents sclerodermatous chronic graft-versus-host disease
- PMID: 33942544
- PMCID: PMC8342231
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.425
Donor Treg expansion by liposomal α-galactosylceramide modulates Tfh cells and prevents sclerodermatous chronic graft-versus-host disease
Abstract
Background and aim: Chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) is a major cause of nonrelapse morbidity and mortality following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) VSports手机版. α-Galactosylceramide (α-GC) is a synthetic glycolipid that is recognized by the invariant T-cell receptor of invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells in a CD1d-restricted manner. Stimulation of iNKT cells by α-GC leads to the production of not only immune-stimulatory cytokines but also immune-regulatory cytokines followed by regulatory T-cell (Treg) expansion in vivo. .
Methods: We investigated the effect of iNKT stimulation by liposomal α-GC just after transplant on the subsequent immune reconstitution and the development of sclerodermatous cGVHD. V体育安卓版.
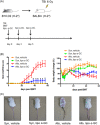
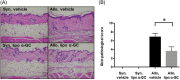
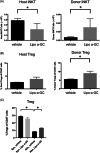
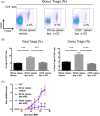
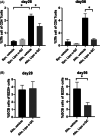
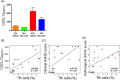
Results: Our study showed that multiple administrations of liposomal α-GC modulated both host- and donor-derived iNKT cell homeostasis and induced an early expansion of donor Tregs. We also demonstrated that the immune modulation of the acute phase was followed by the decreased levels of CXCL13 in plasma and follicular helper T cells in lymph nodes, which inhibited germinal center formation, resulting in the efficient prevention of sclerodermatous cGVHD. V体育ios版.
Conclusions: These data demonstrated an important coordination of T- and B-cell immunity in the pathogenesis of cGVHD and may provide a novel clinical strategy for the induction of immune tolerance after allogeneic HSCT. VSports最新版本.
Keywords: Tfh cells; chronic graft-versus-host disease; hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; iNKT cells; regulatory T cells; α-galactosylceramide V体育平台登录. .
© 2021 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. VSports注册入口.
Conflict of interest statement
Yasuyuki Ishii is the CEO of REGiMMUNE V体育官网入口. The remaining authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests. .
Figures (V体育平台登录)
References
-
- Cutler CS, Koreth J, Ritz J. Mechanistic approaches for the prevention and treatment of chronic GVHD. Blood. 2017;129(1):22‐29. - "VSports注册入口" PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Substances
- VSports app下载 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

