DPP9 sequesters the C terminus of NLRP1 to repress inflammasome activation (VSports手机版)
- PMID: 33731932
- PMCID: PMC8299537
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03350-4
DPP9 sequesters the C terminus of NLRP1 to repress inflammasome activation
Abstract
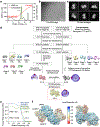
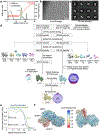
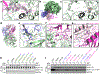
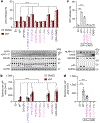
Nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat pyrin-domain containing protein 1 (NLRP1) is an inflammasome sensor that mediates the activation of caspase-1 to induce cytokine maturation and pyroptosis1-4. Gain-of-function mutations of NLRP1 cause severe inflammatory diseases of the skin4-6. NLRP1 contains a function-to-find domain that auto-proteolyses into noncovalently associated subdomains7-9, and proteasomal degradation of the repressive N-terminal fragment of NLRP1 releases its inflammatory C-terminal fragment (NLRP1 CT)10,11. Cytosolic dipeptidyl peptidases 8 and 9 (hereafter, DPP8/DPP9) both interact with NLRP1, and small-molecule inhibitors of DPP8/DPP9 activate NLRP1 by mechanisms that are currently unclear10,12-14. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of the human NLRP1-DPP9 complex alone and with Val-boroPro (VbP), an inhibitor of DPP8/DPP9. The structures reveal a ternary complex that comprises DPP9, full-length NLRP1 and the NLRPT CT. The binding of the NLRP1 CT to DPP9 requires full-length NLRP1, which suggests that NLRP1 activation is regulated by the ratio of NLRP1 CT to full-length NLRP1. Activation of the inflammasome by ectopic expression of the NLRP1 CT is consistently rescued by co-expression of autoproteolysis-deficient full-length NLRP1. The N terminus of the NLRP1 CT inserts into the DPP9 active site, and VbP disrupts this interaction. Thus, VbP weakens the NLRP1-DPP9 interaction and accelerates degradation of the N-terminal fragment10 to induce inflammasome activation. Overall, these data demonstrate that DPP9 quenches low levels of NLRP1 CT and thus serves as a checkpoint for activation of the NLRP1 inflammasome. VSports手机版.
VSports手机版 - Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. H. W. is a co-founder of Ventus Therapeutics. The other authors declare no competing interests V体育安卓版.
Figures


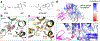




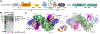

References
-
- Martinon F, Burns K & Tschopp J The Inflammasome: A Molecular Platform Triggering Activation of Inflammatory Caspases and Processing of proIL-β. Mol. Cell 10, 417–426 (2002). - PubMed
"VSports注册入口" Publication types
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
MeSH terms (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
VSports app下载 - Substances
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (VSports手机版)
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"VSports注册入口" Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

