Xylooligosaccharides Increase Bifidobacteria and Lachnospiraceae in Mice on a High-Fat Diet, with a Concomitant Increase in Short-Chain Fatty Acids, Especially Butyric Acid
- PMID: 33724030
- PMCID: PMC8041301
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06279
Xylooligosaccharides Increase Bifidobacteria and Lachnospiraceae in Mice on a High-Fat Diet, with a Concomitant Increase in Short-Chain Fatty Acids, Especially Butyric Acid
Abstract
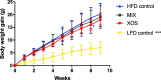
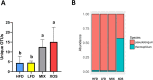
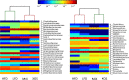
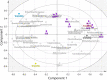
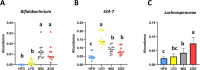
Effects of xylooligosaccharides (XOSs) as well as a mixture of XOS, inulin, oligofructose, and partially hydrolyzed guar gum (MIX) in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD) were studied. Control groups were fed an HFD or a low-fat diet. Special attention was paid to the cecal composition of the gut microbiota and formation of short-chain fatty acids, but metabolic parameters were also documented. The XOS group had significantly higher cecum levels of acetic, propionic, and butyric acids than the HFD group, and the butyric acid content was higher in the XOS than in the MIX group VSports手机版. The cecum microbiota of the XOS group contained more Bifidobacteria, Lachnospiraceae, and S24-7 bacteria than the HFD group. A tendency of lower body weight gain was observed on comparing the XOS and HFD groups. In conclusion, the XOS was shown to be a promising prebiotic candidate. The fiber diversity in the MIX diet did not provide any advantages compared to the XOS diet. .
Keywords: Bifidobacteria; Lachnospiraceae, S24-7; butyrate; high-fat diet; prebiotics; short-chain fatty acids; xylooligosaccharides. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Farias D. d. P.; de Araújo F. F.; Neri-Numa I. A.; Pastore G. M. Prebiotics: Trends in food, health and technological applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 23–35. 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.09.004. - DOI
-
- Jakobsdottir G.; Xu J.; Molin G.; Ahrne S.; Nyman M. High-Fat Diet Reduces the Formation of Butyrate, but Increases Succinate, Inflammation, Liver Fat and Cholesterol in Rats, while Dietary Fibre Counteracts These Effects. PLoS One 2013, 8, e8047610.1371/journal.pone.0080476. - "V体育官网" DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fak F.; Jakobsdottir G.; Kulcinskaja E.; Marungruang N.; Matziouridou C.; Nilsson U.; Stalbrand H.; Nyman M. The Physico-Chemical Properties of Dietary Fibre Determine Metabolic Responses, Short-Chain Fatty Acid Profiles and Gut Microbiota Composition in Rats Fed Low- and High-Fat Diets. PLoS One 2015, 10, e012725210.1371/journal.pone.0127252. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
V体育ios版 - Substances
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

