Deubiquitinating enzyme OTUB1 promotes cancer cell immunosuppression via preventing ER-associated degradation of immune checkpoint protein PD-L1
- PMID: 33328570
- PMCID: PMC8184985
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-020-00700-z
Deubiquitinating enzyme OTUB1 promotes cancer cell immunosuppression via preventing ER-associated degradation of immune checkpoint protein PD-L1
Abstract
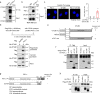
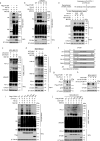
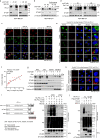
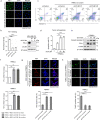
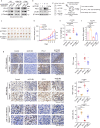
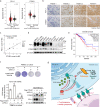
Upregulation of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) helps tumor cells escape from immune surveillance, and therapeutic antibodies targeting PD-1/PD-L1 have shown better patient outcomes only in several types of malignancies. Recent studies suggest that the clinical efficacy of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 treatments is associated with PD-L1 levels; however, the underlying mechanism of high PD-L1 protein levels in cancers is not well defined. Here, we report that the deubiquitinase OTUB1 positively regulates PD-L1 stability and mediates cancer immune responses through the PD-1/PD-L1 axis VSports手机版. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that OTUB1 interacts with and removes K48-linked ubiquitin chains from the PD-L1 intracellular domain in a manner dependent on its deubiquitinase activity to hinder the degradation of PD-L1 through the ERAD pathway. Functionally, depletion of OTUB1 markedly decreases PD-L1 abundance, reduces PD-1 protein binding to the tumor cell surface, and causes increased tumor cell sensitivity to human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs)-mediated cytotoxicity. Meanwhile, OTUB1 ablation-induced PD-L1 destabilization facilitates more CD8+ T cells infiltration and increases the level of IFN-γ in serum to enhance antitumor immunity in mice, and the tumor growth suppression by OTUB1 silencing could be reversed by PD-L1 overexpression. Furthermore, we observe a significant correlation between PD-L1 abundance and OTUB1 expression in human breast carcinoma. Our study reveals OTUB1 as a deubiquitinating enzyme that influences cancer immunosuppression via regulation of PD-L1 stability and may be a potential therapeutic target for cancer immunotherapy. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
V体育ios版 - Figures

References
-
- Zou W, Wolchok JD, Chen L. PD-L1 (B7-H1) and PD-1 pathway blockade for cancer therapy: Mechanisms, response biomarkers, and combinations. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8:328rv324. - "VSports注册入口" PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Han X. Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy of human cancer: past, present, and future. J Clin Invest. 2015;125:3384–91. - PMC (VSports最新版本) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials (VSports注册入口)
Miscellaneous

