"V体育官网入口" Chronic treatment with the (iso-)glutaminyl cyclase inhibitor PQ529 is a novel and effective approach for glomerulonephritis in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 33159802
- PMCID: V体育官网 - PMC8007495
- DOI: V体育2025版 - 10.1007/s00210-020-02013-x
V体育官网 - Chronic treatment with the (iso-)glutaminyl cyclase inhibitor PQ529 is a novel and effective approach for glomerulonephritis in chronic kidney disease
"VSports最新版本" Abstract
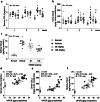
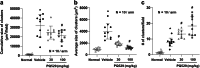
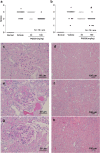
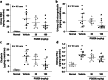
Glomeruli and renal tubule injury in chronic kidney disease (CKD) is reported to involve induction of macrophage activation through the CCL2/CCR2 axis. The effects of inhibitors of the CCL2/CCR2 axis, such as anti-CCL2 antibody and CCR2 antagonist, on kidney function in animal models or humans with kidney dysfunction have been demonstrated. The N-terminal glutamine on immature CCL2 is replaced with pyroglutamate (pE) by glutaminyl cyclase (QC) and isoQC. pE-CCL2 is stable and resistant to peptidases. We hypothesized that inhibiting QC/isoQC activity would lead to the degradation of CCL2, thereby ameliorating CKD and reducing kidney inflammation. To test this hypothesis, we investigated the renoprotective properties of the QC/isoQC inhibitor PQ529 in anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) antibody-induced glomerulonephritis Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rats. Three-week repeated administration of PQ529 (30 and 100 mg/kg, twice daily) significantly reduced the serum and urine CCL2 and urinary protein excretion in a dose-dependent manner. Correlations between the urinary protein level and serum or urinary CCL2 levels were confirmed in tested animals. Repeated administration of PQ529 significantly reduced the expression of CD68, a macrophage marker, in the kidney cortex and mononuclear infiltration into the tubulointerstitium. In addition, decreased levels of urinary KIM-1, β2 microglobulin, and clusterin were detected, suggesting the inhibition of inflammation in both the proximal and distal tubules. These results suggest that PQ529 suppresses the progression of inflammation-induced renal dysfunction by inhibiting the CCL2/CCR2 axis VSports手机版. Inhibition of QC/isoQC may thus be a viable alternative therapeutic approach for treating glomerulonephritis and CKD patients. .
Keywords: CCL2/CCR2 axis; Chronic kidney disease; Glomerulonephritis; PQ529; QC/isoQC inhibitor V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest other than being employees of Astellas Pharma Inc V体育ios版. that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures


References
-
- Cynis H, Rahfeld JU, Stephan A, Kehlen A, Koch B, Wermann M, Demuth HU, Schilling S. Isolation of an isoenzyme of human glutaminyl cyclase: retention in the Golgi complex suggests involvement in the protein maturation machinery. J Mol Biol. 2008;379(5):996–980. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.03.078. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Substances
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育官网" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育官网" Other Literature Sources
Medical (V体育ios版)

