Bile acid toxicity in Paneth cells contributes to gut dysbiosis induced by high-fat feeding
- PMID: 33055426
- PMCID: PMC7605541
- DOI: V体育2025版 - 10.1172/jci.insight.138881
Bile acid toxicity in Paneth cells contributes to gut dysbiosis induced by high-fat feeding
Abstract
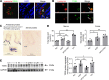
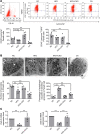
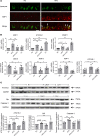
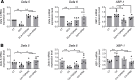
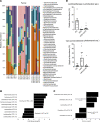
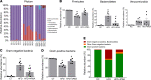
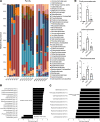
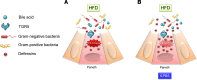
High-fat feeding (HFF) leads to gut dysbiosis through unclear mechanisms. We hypothesize that bile acids secreted in response to high-fat diets (HFDs) may act on intestinal Paneth cells, leading to gut dysbiosis. We found that HFF resulted in widespread taxonomic shifts in the bacteria of the ileal mucosa, characterized by depletion of Lactobacillus and enrichment of Akkermansia muciniphila, Clostridium XIVa, Ruminococcaceae, and Lachnospiraceae, which were prevented by the bile acid binder cholestyramine. Immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization studies showed that G protein-coupled bile acid receptor (TGR5) expressed in Paneth cells was upregulated in the rats fed HFD or normal chow supplemented with cholic acid. This was accompanied by decreased lysozyme+ Paneth cells and α-defensin 5 and 6 and increased expression of XBP-1. Pretreatment with ER stress inhibitor 4PBA or with cholestyramine prevented these changes. Ileal explants incubated with deoxycholic acid or cholic acid caused a decrease in α-defensin 5 and 6 and an increase in XBP-1, which was prevented by TGR5 antibody or 4PBA. In conclusion, this is the first demonstration to our knowledge that TGR5 is expressed in Paneth cells. HFF resulted in increased bile acid secretion and upregulation of TGR5 expression in Paneth cells. Bile acid toxicity in Paneth cells contributes to gut dysbiosis induced by HFF VSports手机版. .
Keywords: Defensins; Gastroenterology; Obesity V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


"V体育安卓版" References
-
- Albenberg LG, Wu GD. Diet and the intestinal microbiome: associations, functions, and implications for health and disease. Gastroenterology. 2014;146(6):1564–1572. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.01.058. - "V体育安卓版" DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Just S, et al. The gut microbiota drives the impact of bile acids and fat source in diet on mouse metabolism. Microbiome. 2018;6(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0510-8. - VSports - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
MeSH terms (VSports app下载)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Substances (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Supplementary concepts
- "VSports" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (VSports最新版本)
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (VSports在线直播)
Molecular Biology Databases

