Drug-induced hepatic steatosis in absence of severe mitochondrial dysfunction in HepaRG cells: proof of multiple mechanism-based toxicity
- PMID: 32535746
- PMCID: V体育平台登录 - PMC8012331
- DOI: 10.1007/s10565-020-09537-1
Drug-induced hepatic steatosis in absence of severe mitochondrial dysfunction in HepaRG cells: proof of multiple mechanism-based toxicity
VSports最新版本 - Abstract
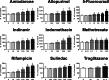
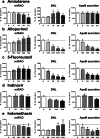
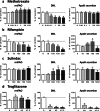
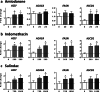
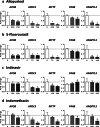
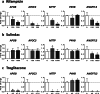
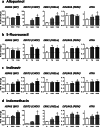
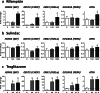
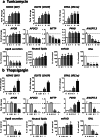
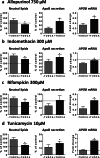
Steatosis is a liver lesion reported with numerous pharmaceuticals. Prior studies showed that severe impairment of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation (mtFAO) constantly leads to lipid accretion in liver. However, much less is known about the mechanism(s) of drug-induced steatosis in the absence of severe mitochondrial dysfunction, although previous studies suggested the involvement of mild-to-moderate inhibition of mtFAO, increased de novo lipogenesis (DNL), and impairment of very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) secretion. The objective of our study, mainly carried out in human hepatoma HepaRG cells, was to investigate these 3 mechanisms with 12 drugs able to induce steatosis in human: amiodarone (AMIO, used as positive control), allopurinol (ALLO), D-penicillamine (DPEN), 5-fluorouracil (5FU), indinavir (INDI), indomethacin (INDO), methimazole (METHI), methotrexate (METHO), nifedipine (NIF), rifampicin (RIF), sulindac (SUL), and troglitazone (TRO). Hepatic cells were exposed to drugs for 4 days with concentrations decreasing ATP level by less than 30% as compared to control and not exceeding 100 × Cmax. Among the 12 drugs, AMIO, ALLO, 5FU, INDI, INDO, METHO, RIF, SUL, and TRO induced steatosis in HepaRG cells. AMIO, INDO, and RIF decreased mtFAO. AMIO, INDO, and SUL enhanced DNL VSports手机版. ALLO, 5FU, INDI, INDO, SUL, RIF, and TRO impaired VLDL secretion. These seven drugs reduced the mRNA level of genes playing a major role in VLDL assembly and also induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Thus, in the absence of severe mitochondrial dysfunction, drug-induced steatosis can be triggered by different mechanisms, although impairment of VLDL secretion seems more frequently involved, possibly as a consequence of ER stress. .
Keywords: Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Fatty acid oxidation; Lipogenesis; Mitochondria; Steatosis; Very low-density lipoprotein V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
J. A. , S. B. , J. M. , P. -J. F V体育ios版. , D. L. G. , Y. D. , Y. L. , K. B. , and B. F. declare that they have no conflict of interest in relation to this work. N. B. and A. B. -S. are co-founders of MITOLOGICS S. A. S. R. L. is an employee of MITOLOGICS S. A. S.
Figures
References
-
- Allard J, Le Guillou D, Begriche K, Fromenty B. Drug-induced liver injury in obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Adv Pharmacol. 2019;85:75–107. - PubMed
-
- Amacher DE, Chalasani N. Drug-induced hepatic steatosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2014;34(2):205–214. - V体育2025版 - PubMed
-
- Anthérieu S, Rogue A, Fromenty B, Guillouzo A, Robin MA. Induction of vesicular steatosis by amiodarone and tetracycline is associated with up-regulation of lipogenic genes in HepaRG cells. Hepatology. 2011;53(6):1895–1905. - PubMed
-
- Baiceanu A, Mesdom P, Lagouge M, Foufelle F. Endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis in hepatic steatosis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12(12):710–722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
"VSports在线直播" Substances
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育平台登录)
Research Materials

