V体育安卓版 - Mechanisms underlying CD19-positive ALL relapse after anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy and associated strategies
- PMID: 32514351
- PMCID: PMC7254656
- DOI: "VSports注册入口" 10.1186/s40364-020-00197-1
Mechanisms underlying CD19-positive ALL relapse after anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy and associated strategies
Abstract
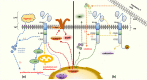
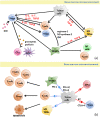
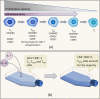
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy, especially anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy, has shown remarkable anticancer activity in patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia, demonstrating an inspiring complete remission rate. However, with extension of the follow-up period, the limitations of this therapy have gradually emerged. Patients are at a high risk of early relapse after achieving complete remission. Although there are many studies with a primary focus on the mechanisms underlying CD19- relapse related to immune escape, early CD19+ relapse owing to poor in vivo persistence and impaired efficacy accounts for a larger proportion of the high relapse rate. However, the mechanisms underlying CD19+ relapse are still poorly understood. Herein, we discuss factors that could become obstacles to improved persistence and efficacy of CAR T cells during production, preinfusion processing, and in vivo interactions in detail. Furthermore, we propose potential strategies to overcome these barriers to achieve a reduced CD19+ relapse rate and produce prolonged survival in patients after CAR T cell therapy VSports手机版. .
Keywords: Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL); CAR T cell therapy; Chimeric antigen receptor; Mechanism; Positive relapse; Strategy V体育安卓版. .
© The Author(s) 2020.
VSports注册入口 - Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
V体育安卓版 - Figures

"V体育2025版" References
Publication types
VSports - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

