Cortical Thymocytes Along With Their Selecting Ligands Are Required for the Further Thymic Maturation of NKT Cells in Mice (V体育平台登录)
- PMID: 32457751
- PMCID: PMC7221135
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00815
Cortical Thymocytes Along With Their Selecting Ligands Are Required for the Further Thymic Maturation of NKT Cells in Mice (V体育安卓版)
Abstract
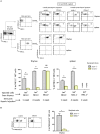
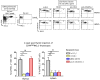
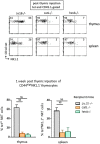
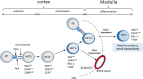
Following positive selection, NKT cell precursors enter an "NK-like" program and progress from an NK- to an NK+ maturational stage to give rise to NKT1 cells. Maturation takes place in the thymus or after emigration of NK- NKT cells to the periphery. In this study, we followed the fate of injected NKT cells at the NK- stage of their development in the thymus of a series of mice with differential CD1d expression VSports手机版. Our results indicate that CD1d-expressing cortical thymocytes, and not epithelial cells, macrophages, or dendritic cells, are necessary and sufficient to promote the maturation of thymic NKT1 cells. Migration out of the thymus of NK- NKT cells occurred in the absence of CD1d expression, however, CD1d expression is required for maturation in peripheral organs. We also found that the natural ligand Isoglobotriosylceramide (iGb3), and the cysteine protease Cathepsin L, both localizing with CD1d in the endosomal compartment and crucial for NKT cell positive selection, are also required for NK- to NK+ NKT cell transition. Overall, our study indicates that the maturational transition of NKT cells require continuous TCR/CD1d interactions and suggest that these interactions occur in the thymic cortex where DP cortical thymocytes are located. We thus concluded that key components necessary for positive selection of NKT cells are also required for subsequent maturation. .
Keywords: CD1d; NKT1; cathepsin L; development; iGb3; plck; thymus V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2020 Klibi and Benlagha.
V体育官网入口 - Figures
References
-
- Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol. (2007) 25:297–336. - PubMed
-
- Bendelac A, Rivera MN, Park SH, Roark JH. Mouse CD1-specific NK1 T cells: development, specificity, and function. Annu Rev Immunol. (1997) 15:535–62. - PubMed
-
- Benlagha K, Weiss A, Beavis A, Teyton L, Bendelac A. In vivo identification of glycolipid antigen-specific T cells using fluorescent CD1d tetramers. J Exp Med. (2000) 191:1895–903. - PMC (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
-
- Benlagha K, Kyin T, Beavis A, Teyton L, Bendelac A. A thymic precursor to the NK T cell lineage. Science. (2002) 296:553–5. - PubMed
-
- Townsend MJ, Weinmann AS, Matsuda JL, Salomon R, Farnham PJ, Biron CA, et al. T-bet regulates the terminal maturation and homeostasis of NK and Valpha14i NKT cells. Immunity. (2004) 20:477–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
Substances
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
"V体育安卓版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育平台登录" Molecular Biology Databases

