Expression of immune checkpoints and T cell exhaustion markers in early and advanced stages of colorectal cancer
- PMID: 32393998
- PMCID: PMC7511277
- DOI: "V体育2025版" 10.1007/s00262-020-02593-w
Expression of immune checkpoints and T cell exhaustion markers in early and advanced stages of colorectal cancer
V体育ios版 - Abstract
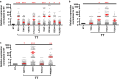
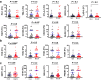
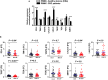
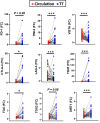
Despite recent advances in colorectal cancer (CRC) treatment, a large proportion of patients show limited responses to therapies, especially in advanced stages. There is an urgent need to identify prognostic biomarkers and/or therapeutic targets in advanced stages, aiming to improve the efficacy of current treatments. We aimed to determine prognostic biomarkers in tumor tissue and circulation of CRC patients, with a special focus on T cell exhaustion markers. We found that mRNA levels of PD-1, TIM-3, CTLA-4, TIGIT, CD160, CD244, KLRG1, TOX2, TOX3, Ki-67, and PRDM1 were elevated in CRC tumor tissues. We also investigated differences in gene expression between early and advanced disease stages. We found that TOX and potentially TIM-3, CTLA-4, VISTA, TIGIT, KLRG1, TOX2, SIRT1, Ki-67, and Helios mRNA levels in tumor tissue were elevated in advanced disease stages, suggesting their potential roles in CRC progression. In contrast, PD-1 and CD160 levels in tumor tissue were downregulated in advanced stages. In the circulation of CRC patients, mRNA levels of PD-1, VISTA and LAG-3 were higher than those of healthy individuals. Moreover, in circulation, PD-1, CTLA-4 and TIGIT mRNA levels were reduced in advanced stages. Interestingly, levels of PD-1 in both tumor tissue and circulation were reduced in advanced stages, suggesting that targeting PD-1 in patients with advanced stages could be less effective. Altogether, these findings suggest some potential T cell exhaustion markers that could be utilized as prognostic biomarkers and/or therapeutic targets for CRC. However, further investigations and validations in larger cohorts are required to confirm these findings. VSports手机版.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Immune checkpoints; Prognostic biomarker; T cell exhaustion; Therapeutic target. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
VSports app下载 - Figures
References (VSports app下载)
-
- Xia A, Zhang Y, Xu J, Yin T, Lu XJ. T cell dysfunction in cancer immunity and immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1719. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01719. - VSports注册入口 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saleh R, Elkord E. Treg-mediated acquired resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Lett. 2019;457:168–179. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.05.003. - "V体育官网入口" DOI - PubMed
-
- Saleh R, Elkord E. Acquired resistance to cancer immunotherapy: Role of tumor-mediated immunosuppression. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019 doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.07.017. - V体育ios版 - DOI - PubMed
V体育官网 - MeSH terms
- VSports - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
Substances
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (VSports注册入口)
Full Text Sources (VSports)
VSports app下载 - Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

