The Bacterium VSports app下载 - Akkermansia muciniphila: A Sentinel for Gut Permeability and Its Relevance to HIV-Related Inflammation
- PMID: 32328074
- PMCID: PMC7160922
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00645
The Bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila: A Sentinel for Gut Permeability and Its Relevance to HIV-Related Inflammation
Abstract
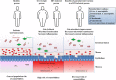
Gut dysbiosis, namely dysregulation of the intestinal microbiota, and increased gut permeability lead to enhanced inflammation and are commonly seen in chronic conditions such as obesity and aging. In people living with HIV (PLWH), several lines of evidence suggest that a depletion of gut CD4 T-cells is associated with gut dysbiosis, microbial translocation and systemic inflammation. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) rapidly controls viral replication, which leads to CD4 T-cell recovery and control of the disease. However, gut dysbiosis, epithelial damage and microbial translocation persist despite ART, increasing risk of developing inflammatory non-AIDS comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, liver steatosis and cancer. In addition to ART, an emerging research priority is to discover strategies to improve the gut microbial composition and intestinal barrier function. Probiotic interventions have been extensively used with controversial benefits in humans VSports手机版. Encouragingly, within the last decade, the intestinal symbiotic bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila has emerged as the "sentinel of the gut. " A lower abundance of A. muciniphila has been shown in diabetic and obese people as well as in PLWH. Interventions with high levels of polyphenols such as tea or diets rich in fruit, the antibiotic vancomycin and the antidiabetic drug metformin have been shown to increase A. muciniphila abundance, contributing to improved metabolic function in diabetic and obese individuals. We hypothesize that gut microbiota rich in A. muciniphila can reduce microbial translocation and inflammation, preventing occurrences of non-AIDS comorbidities in PLWH. To this aim, we will discuss the protective effect of A. muciniphila and its potential applications, paving the way toward novel therapeutic strategies to improve gut health in PLWH. .
Keywords: Akkermansia muciniphila; HIV; epithelial gut damage; inflammation; microbial translocation V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2020 Ouyang, Lin, Isnard, Fombuena, Peng, Marette, Routy, Messaoudene, Chen and Routy V体育ios版. .
Figures
"VSports app下载" References
-
- Vinolo MA, Rodrigues HG, Nachbar RT, Curi R. Regulation of inflammation by short chain fatty acids. Nutrients. (2011) 3:858–76. 10.3390/nu3100858 - "V体育官网" DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types (VSports在线直播)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
"V体育平台登录" Substances
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Supplementary concepts
- Actions (V体育官网)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports手机版" Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials (V体育官网入口)