V体育官网入口 - A phase 1 trial of itacitinib, a selective JAK1 inhibitor, in patients with acute graft-versus-host disease
- PMID: 32324888
- PMCID: PMC7189299
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019001043
"V体育官网" A phase 1 trial of itacitinib, a selective JAK1 inhibitor, in patients with acute graft-versus-host disease
"V体育官网" Abstract
Acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is a primary cause of nonrelapse mortality and a major barrier to successful transplant outcomes VSports手机版. Itacitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK)1-selective inhibitor that has demonstrated efficacy in preclinical models of aGVHD. We report results from the first registered study of a JAK inhibitor in patients with aGVHD. This was an open-label phase 1 study enrolling patients aged ≥18 years with first HCT from any source who developed grade IIB to IVD aGVHD. Patients with steroid-naive or steroid-refractory aGVHD were randomized 1:1 to itacitinib 200 mg or 300 mg once daily plus corticosteroids. The primary endpoint was safety and tolerability; day 28 overall response rate (ORR) was the main secondary endpoint. Twenty-nine patients (200 mg, n = 14; 300 mg, n = 15) received ≥1 dose of itacitinib and were included in safety and efficacy assessments. One dose-limiting toxicity was reported (grade 3 thrombocytopenia attributed to GVHD progression in a patient receiving 300 mg itacitinib with preexisting thrombocytopenia). The most common nonhematologic treatment-emergent adverse event was diarrhea (48. 3%, n = 14); anemia occurred in 11 patients (38%). ORR on day 28 for all patients in the 200-mg and 300-mg groups was 78. 6% and 66. 7%, respectively. Day 28 ORR was 75. 0% for patients with treatment-naive aGVHD and 70. 6% in those with steroid-refractory aGVHD. All patients receiving itacitinib decreased corticosteroid use over time. In summary, itacitinib was well tolerated and demonstrated encouraging efficacy in patients with steroid-naive or steroid-refractory aGVHD, warranting continued clinical investigations. This trial was registered at www. clinicaltrials. gov as #NCT02614612. .
© 2020 by The American Society of Hematology. V体育安卓版.
V体育官网 - Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M. A. S. received honoraria and research funding from Incyte Corporation. H. J. K. served on an advisory board and received research funding from Incyte Corporation. M. J. received research funding from Therakos, Janssen, and Incyte Corporation. H. A V体育ios版. and G. J. S. received research funding from Incyte Corporation. K. S. served as a consultant for RiverVest and Kinetic River and is a coinventor on a patent related to CART therapy. J. C. received honorarium from Incyte Corporation, received research funding from Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, and served as a consultant for Daewoong Pharmaceutical. M. C. A. , Y. Y. , P. L. , N. S. , and M. P. are employees and stockholders of Incyte Corporation. M. -A. P. received honoraria from AbbVie, Bellicum, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte Corporation, Merck, Novartis, Nektar Therapeutics, Omeros, and Takeda; served on data and safety monitoring boards for Servier and Medigene; served on scientific advisory boards for MolMed and NexImmune; and has received research support for clinical trials from Incyte Corporation, Kite/Gilead, and Miltenyl Biotec. Y. -B. C. served as a consultant for Incyte Corporation and Takeda and received research funding from Incyte Corporation and Novartis Pharmaceuticals. J. F. D. served on advisory boards for Incyte Corporation, CellWorks, Macrogenics, Amphivena, Arch, Rivervest, and Bioline and is a cofounder of Magenta Therapeutics and WUGen. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures (V体育官网)
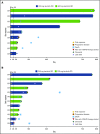


References (V体育2025版)
-
- D’Souza A, Fretham C Current uses and outcomes of hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT): CIBMTR summary slides, 2018. https://www.cibmtr.org. Accessed 12 April 2019.
-
- Vogelsang GB, Lee L, Bensen-Kennedy DM. Pathogenesis and treatment of graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplant. Annu Rev Med. 2003;54(1):29-52. - V体育安卓版 - PubMed
-
- Ferrara JL, Levine JE, Reddy P, Holler E. Graft-versus-host disease. Lancet. 2009;373(9674):1550-1561. - VSports注册入口 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gooley TA, Chien JW, Pergam SA, et al. . Reduced mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(22):2091-2101. - PMC (V体育安卓版) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
V体育安卓版 - Substances
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
Associated data
"V体育平台登录" Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
V体育官网入口 - Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials (V体育官网入口)
Miscellaneous

