Abnormal Cullin1 neddylation-mediated p21 accumulation participates in the pathogenesis of recurrent spontaneous abortion by regulating trophoblast cell proliferation and differentiation
- PMID: 32186736
- PMCID: PMC7227182
- DOI: "V体育平台登录" 10.1093/molehr/gaaa021
Abnormal Cullin1 neddylation-mediated p21 accumulation participates in the pathogenesis of recurrent spontaneous abortion by regulating trophoblast cell proliferation and differentiation
Abstract
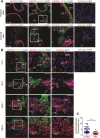
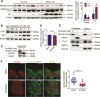
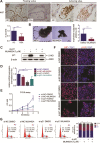
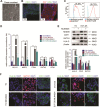
The study explores the role of neddylation in early trophoblast development and its alteration during the pathogenesis of recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA). Immunofluorescence and western blot were conducted to evaluate the expression pattern of NEDD8 protein in the first-trimester placentas of healthy control and RSA patients. Neddylated-cullins, especially neddylated-cullin1, were downregulated and their substrate, p21, was accumulated in RSA samples. NEDD8 cytoplasmic recruitment was observed in extravillous trophoblast (EVT) progenitors of RSA placentas. Consistent with the results of clinical samples, neddylation inhibition using MLN4924 in trophoblast cell lines caused obvious p21 accumulation and free NEDD8 cytoplasmic recruitment VSports手机版. Further in vitro study demonstrated neddylation inhibition attenuated proliferation of Jeg-3 cells via p21 accumulation. Moreover, when trophoblast stem (TS) cells derived from first-trimester placentas were cultured for differentiation analyses. MLN4924 impaired the differentiation of TS cells towards EVTs by downregulating HLA-G and GATA3. p21 knockdown could partly rescue MLN4924-suppressed HLA-G and GATA3 expression. In conclusion, cullin1 neddylation-mediated p21 degradation is required for trophoblast proliferation and can affect trophoblast plasticity by affecting HLA-G and GATA3 expression. The results provide insights into the pathological mechanism of RSA and the biological regulation of trophoblast development. .
Keywords: NEDD8; neddylation; p21; recurrent spontaneous abortion; trophoblast stem cell V体育安卓版. .
© The Author(s) 2020 V体育ios版. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. .
V体育官网 - Figures

References
-
- Baek KH, Lee EJ, Kim YS. Recurrent pregnancy loss: the key potential mechanisms. Trends Mol Med 2007;13:310–317. - PubMed
-
- Bischof P, Irminger-Finger I. The human cytotrophoblastic cell, a mononuclear chameleon. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2005;37:1–16. - PubMed (VSports app下载)
-
- Brownell JE, Sintchak MD, Gavin JM, Liao H, Bruzzese FJ, Bump NJ, Soucy TA, Milhollen MA, Yang X, Burkhardt AL et al. . Substrate-assisted inhibition of ubiquitin-like protein-activating enzymes: the NEDD8 E1 inhibitor MLN4924 forms a NEDD8-AMP mimetic in situ. Mol Cell 2010;37:102–111. - PubMed
-
- Carrington B, Sacks G, Regan L. Recurrent miscarriage: pathophysiology and outcome. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 2005;17:591–597. - PubMed
-
- Chen P, Hu T, Liang Y, Li P, Chen X, Zhang J, Ma Y, Hao Q, Wang J, Zhang P et al. . Neddylation inhibition activates the extrinsic apoptosis pathway through ATF4-CHOP-DR5 Axis in human esophageal cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 2016;22:4145–4157. - VSports手机版 - PubMed
"VSports手机版" Publication types
- Actions (VSports)
MeSH terms
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Substances
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources (VSports注册入口)
Full Text Sources
Research Materials (VSports)
Miscellaneous

