International Olympic Committee consensus statement: methods for recording and reporting of epidemiological data on injury and illness in sport 2020 (including STROBE Extension for Sport Injury and Illness Surveillance (STROBE-SIIS))
- PMID: 32071062
- PMCID: PMC7146946
- DOI: 10.1136/bjsports-2019-101969
International Olympic Committee consensus statement: methods for recording and reporting of epidemiological data on injury and illness in sport 2020 (including STROBE Extension for Sport Injury and Illness Surveillance (STROBE-SIIS))
VSports app下载 - Abstract
Injury and illness surveillance, and epidemiological studies, are fundamental elements of concerted efforts to protect the health of the athlete. To encourage consistency in the definitions and methodology used, and to enable data across studies to be compared, research groups have published 11 sport-specific or setting-specific consensus statements on sports injury (and, eventually, illness) epidemiology to date VSports手机版. Our objective was to further strengthen consistency in data collection, injury definitions and research reporting through an updated set of recommendations for sports injury and illness studies, including a new Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) checklist extension. The IOC invited a working group of international experts to review relevant literature and provide recommendations. The procedure included an open online survey, several stages of text drafting and consultation by working groups and a 3-day consensus meeting in October 2019. This statement includes recommendations for data collection and research reporting covering key components: defining and classifying health problems; severity of health problems; capturing and reporting athlete exposure; expressing risk; burden of health problems; study population characteristics and data collection methods. Based on these, we also developed a new reporting guideline as a STROBE Extension-the STROBE Sports Injury and Illness Surveillance (STROBE-SIIS). The IOC encourages ongoing in- and out-of-competition surveillance programmes and studies to describe injury and illness trends and patterns, understand their causes and develop measures to protect the health of the athlete. Implementation of the methods outlined in this statement will advance consistency in data collection and research reporting. .
Keywords: consensus statement; epidemiology; illness; injuries; methodology V体育安卓版. .
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC V体育ios版. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ. .
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: BR receives payment for duties as Editor-in-Chief of the The Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine VSports最新版本. KK is the Editor-in-Chief of the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Figures
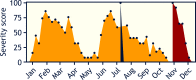
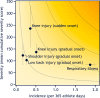
References
-
- Mountjoy M, Junge A, Alonso JM, et al. . Consensus statement on the methodology of injury and illness surveillance in FINA (aquatic sports): Table 1. Br J Sports Med 2016;50:590–6. 10.1136/bjsports-2015-095686 - DOI (V体育2025版) - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育ios版)
"V体育平台登录" MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical (V体育ios版)
