EZH2 Inhibition Sensitizes CARM1-High, Homologous Recombination Proficient Ovarian Cancers to PARP Inhibition
- PMID: 32004442
- PMCID: PMC7155421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.12.015
EZH2 Inhibition Sensitizes CARM1-High, Homologous Recombination Proficient Ovarian Cancers to PARP Inhibition
Abstract
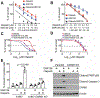
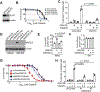
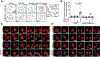
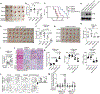
In response to DNA double-strand breaks, MAD2L2-containing shieldin complex plays a critical role in the choice between homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ)-mediated repair. Here we show that EZH2 inhibition upregulates MAD2L2 and sensitizes HR-proficient epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) to poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor in a CARM1-dependent manner. CARM1 promotes MAD2L2 silencing by driving the switch from the SWI/SNF complex to EZH2 through methylating the BAF155 subunit of the SWI/SNF complex on the MAD2L2 promoter. EZH2 inhibition upregulates MAD2L2 to decrease DNA end resection, which increases NHEJ and chromosomal abnormalities, ultimately causing mitotic catastrophe in PARP inhibitor treated HR-proficient cells. Significantly, EZH2 inhibitor sensitizes CARM1-high, but not CARM-low, EOCs to PARP inhibitors in both orthotopic and patient-derived xenografts. VSports手机版.
Keywords: BAF155; CARM1; EZH2 inhibitors; MAD2L2 (REV7); PARP inhibitors; SWI/SNF; epithelial ovarian cancer; homologous recombination (HR); non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ); polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2); shieldin V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. V体育ios版.
Conflict of interest statement (V体育ios版)
Declaration of Interests S. K. and R. Z. are co-inventors on a patent application covering the use of EZH2 inhibitors in CARM1-expressing cancers VSports最新版本. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Opening a Door to PARP Inhibitor-Induced Lethality in HR-Proficient Human Tumor Cells.Cancer Cell. 2020 Feb 10;37(2):139-140. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.01.005. Cancer Cell. 2020. PMID: 32049041
References
-
- Cao R, and Zhang Y (2004). The functions of E(Z)/EZH2-mediated methylation of lysine 27 in histone H3. Curr Opin Genet Dev 14, 155–164. - PubMed
Publication types (VSports注册入口)
V体育官网入口 - MeSH terms
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Substances
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

