V体育安卓版 - The MAGIC algorithm probability is a validated response biomarker of treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease
- PMID: 31816061
- PMCID: V体育平台登录 - PMC6963240
- DOI: "V体育ios版" 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000791
The MAGIC algorithm probability is a validated response biomarker of treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease
Abstract
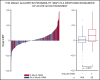
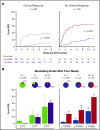
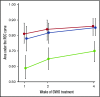
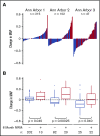
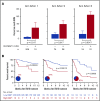
The Mount Sinai Acute GVHD International Consortium (MAGIC) algorithm probability (MAP), derived from 2 serum biomarkers, measures damage to crypts in the gastrointestinal tract during graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) VSports手机版. We hypothesized that changes in MAP after treatment could validate it as a response biomarker. We prospectively collected serum samples and clinical stages of acute GVHD from 615 patients receiving hematopoietic cell transplantation in 20 centers at initiation of first-line systemic treatment and 4 weeks later. We computed MAPs and clinical responses and compared their abilities to predict 6-month nonrelapse mortality (NRM) in the validation cohort (n = 367). After 4 weeks of treatment, MAPs predicted NRM better than the change in clinical symptoms in all patients and identified 2 groups with significantly different NRM in both clinical responders (40% vs 12%, P < . 0001) and nonresponders (65% vs 25%, P < . 0001). MAPs successfully reclassified patients for NRM risk within every clinical grade of acute GVHD after 4 weeks of treatment. At the beginning of treatment, patients with a low MAP that rose above the threshold of 0. 290 after 4 weeks of treatment had a significant increase in NRM, whereas patients with a high MAP at onset that fell below that threshold after treatment had a striking decrease in NRM that translated into clear differences in overall survival. We conclude that a MAP measured before and after treatment of acute GVHD is a response biomarker that predicts long-term outcomes more accurately than change in clinical symptoms. MAPs have the potential to guide therapy for acute GVHD and may function as a useful end point in clinical trials. .
© 2019 by The American Society of Hematology V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: U. M. , J. E. L. , and J. L. M. F. are coinventors on a GVHD biomarker patent V体育ios版. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
V体育ios版 - References
-
- Ferrara JLM, Levine JE, Reddy P, Holler E. Graft-versus-host disease. Lancet. 2009;373(9674):1550-1561. - "VSports最新版本" PMC - PubMed
-
- Zeiser R, Blazar BR. Acute graft-versus-host disease - biologic process, prevention, and therapy. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(22):2167-2179. - "V体育安卓版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Jagasia M, Arora M, Flowers MED, et al. . Risk factors for acute GVHD and survival after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;119(1):296-307. - "VSports app下载" PMC - PubMed
-
- MacMillan ML, Weisdorf DJ, Wagner JE, et al. . Response of 443 patients to steroids as primary therapy for acute graft-versus-host disease: comparison of grading systems. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2002;8(7):387-394. - PubMed (VSports)
-
- MacMillan ML, DeFor TE, Weisdorf DJ. The best endpoint for acute GVHD treatment trials. Blood. 2010;115(26):5412-5417. - VSports手机版 - PubMed
Publication types
VSports注册入口 - MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Substances
- VSports - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (VSports注册入口)
Other Literature Sources

