"VSports app下载" Pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) induced by cigarette smoke
- PMID: 31737341
- PMCID: PMC6831915
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2019.10.43
Pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) induced by cigarette smoke
Abstract
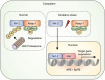
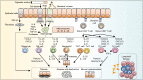
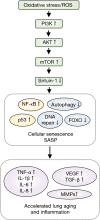
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common respiratory disease that is characterized by functional and structural alterations primarily caused by long-term inhalation of harmful particles. Cigarette smoke (CS) induces airway inflammation in COPD, which is known to persist even after smoking cessation. This review discusses the basic pathogenesis of COPD, with particular focus on an endogenous protective mechanism against oxidative stress via Nrf2, altered immune response of the airway inflammatory cells, exaggerated cellular senescence of the lung structural cells, and cell death with expanded inflammation. Recently, CS-induced mitochondria autophagy is reported to initiate programmed necrosis (necroptosis). Necroptosis is a new concept of cell death which is driven by a defined molecular pathway along with exaggerated inflammation. This new cell death mechanism is of importance due to its ability to produce more inflammatory substances during the process of epithelial death, contributing to persistent airway inflammation that cannot be explained by apoptosis-derived cell death VSports手机版. Autophagy is an auto-cell component degradation system executed by lysosomes that controls protein and organelle degradation for successful homeostasis. As well as in the process of necroptosis, autophagy is also observed during cellular senescence. Aging of the lungs results in the acquisition of senescence-associated secretory phenotypes (SASP) that are known to secrete inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, and matrix metalloproteinases resulting in chronic low-grade inflammation. In future research, we intend to highlight the genetic and epigenetic approaches that can facilitate the understanding of disease susceptibility. The goal of precision medicine is to establish more accurate diagnosis and treatment methods based on the patient-specific pathogenic characteristics. This review provides insights into CS-induced COPD pathogenesis, which contributes to a very complex disease. Investigating the mechanism of developing COPD, along with the availability of the particular inhibitors, will lead to new therapeutic approaches in COPD treatment. .
Keywords: Airway inflammation; autophagy; cellular senescence; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); necroptosis; oxidative stress V体育安卓版. .
2019 Journal of Thoracic Disease V体育ios版. All rights reserved. .
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Wang Y, Xu J, Meng Y, et al. Role of inflammatory cells in airway remodeling in COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2018;13:3341-8. 10.2147/COPD.S176122 - "VSports注册入口" DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
"V体育官网" Full Text Sources
Research Materials
