Irradiation or temozolomide chemotherapy enhances anti-CD47 treatment of glioblastoma
- PMID: 31547758
- PMCID: PMC7016411
- DOI: 10.1177/1753425919876690
V体育安卓版 - Irradiation or temozolomide chemotherapy enhances anti-CD47 treatment of glioblastoma
Abstract
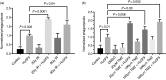
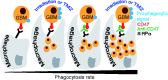
Irradiation and temozolomide (TMZ) chemotherapy are the current standard treatments for glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), but they are associated with toxicity and limited efficacy VSports手机版. Recently, these standard therapies have been used to enhance immunotherapy against GBM. Immunotherapy using the anti-CD47 (immune checkpoint inhibitor) treatment has shown promise in treating multiple tumor types, including GBM. The goal of this current work was to test whether irradiation or TMZ chemotherapy could enhance anti-CD47 treatment against GBM. Our results showed that irradiation and TMZ each significantly enhanced anti-CD47-mediated phagocytosis of GBM cells in vitro. Furthermore, mice engrafted with human GBM that received anti-CD47 combined with focal irradiation or TMZ treatment showed a significant increase in the survival rate compared to those that received a single treatment. The tumor growth in mice that received both anti-CD47 and irradiation was significantly less than that of groups that received either anti-CD47 or focal irradiation. The results from this study may support future use of anti-CD47 treatment in combination with irradiation or chemotherapy to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of GBM treatment. .
Keywords: Glioblastoma; anti-CD47; irradiation; macrophages; phagocytosis; temozolomide V体育安卓版. .
Figures
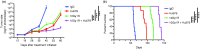

References
-
- Razavi SM, Lee KE, Jin BE, et al. Immune evasion strategies of glioblastoma. Front Surg 2016; 3: 11. - V体育ios版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 987–996. - V体育ios版 - PubMed
-
- Gholamin S, Mitra SS, Feroze AH, et al. Disrupting the CD47-SIRPalpha anti-phagocytic axis by a humanized anti-CD47 antibody is an efficacious treatment for malignant pediatric brain tumors. Sci Transl Med 2017; 9. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育ios版)
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Substances
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

