Salmonella enterica Effectors SifA, SpvB, SseF, SseJ, and SteA Contribute to Type III Secretion System 1-Independent Inflammation in a Streptomycin-Pretreated Mouse Model of Colitis
- PMID: 31235639
- PMCID: "V体育2025版" PMC6704597
- DOI: "V体育2025版" 10.1128/IAI.00872-18
Salmonella enterica Effectors SifA, SpvB, SseF, SseJ, and SteA Contribute to Type III Secretion System 1-Independent Inflammation in a Streptomycin-Pretreated Mouse Model of Colitis
Abstract
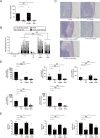
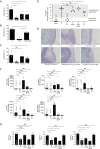
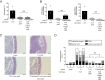
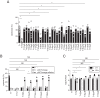
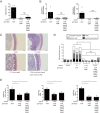
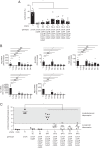
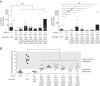
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium) induces inflammatory changes in the ceca of streptomycin-pretreated mice. In this mouse model of colitis, the type III secretion system 1 (T3SS-1) has been shown to induce rapid inflammatory change in the cecum at early points, 10 to 24 h after infection. Five proteins, SipA, SopA, SopB, SopD, and SopE2, have been identified as effectors involved in eliciting intestinal inflammation within this time range. In contrast, a T3SS-1-deficient strain was shown to exhibit inflammatory changes in the cecum at 72 to 120 h postinfection. However, the effectors eliciting T3SS-1-independent inflammation remain to be clarified. In this study, we focused on two T3SS-2 phenotypes, macrophage proliferation and cytotoxicity, to identify the T3SS-2 effectors involved in T3SS-1-independent inflammation. We identified a mutant strain that could not induce cytotoxicity in a macrophage-like cell line and that reduced intestinal inflammation in streptomycin-pretreated mice. We also identified five T3SS-2 effectors, SifA, SpvB, SseF, SseJ, and SteA, associated with T3SS-1-independent macrophage cytotoxicity. We then constructed a strain lacking T3SS-1 and all the five T3SS-2 effectors, termed T1S5 VSports手机版. The S. Typhimurium T1S5 strain significantly reduced cytotoxicity in macrophages in the same manner as a mutant invA spiB strain (T1T2). Finally, the T1S5 strain elicited no inflammatory changes in the ceca of streptomycin-pretreated mice. We conclude that these five T3SS-2 effectors contribute to T3SS-1-independent inflammation. .
Keywords: Salmonella; cytotoxicity; inflammation; type III effectors. V体育安卓版.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology. V体育ios版.
Figures
"V体育安卓版" References
-
- Coombes BK, Coburn BA, Potter AA, Gomis S, Mirakhur K, Li Y, Finlay BB. 2005. Analysis of the contribution of Salmonella pathogenicity islands 1 and 2 to enteric disease progression using a novel bovine ileal loop model and a murine model of infectious enterocolitis. Infect Immun 73:7161–7169. doi:10.1128/IAI.73.11.7161-7169.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hapfelmeier S, Müller AJ, Stecher B, Kaiser P, Barthel M, Endt K, Eberhard M, Robbiani R, Jacobi CA, Heikenwalder M, Kirschning C, Jung S, Stallmach T, Kremer M, Hardt WD. 2008. Microbe sampling by mucosal dendritic cells is a discrete, MyD88-independent step in ΔinvG S. Typhimurium colitis. J Exp Med 205:437–450. doi:10.1084/jem.20070633. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang S, Santos RL, Tsolis RM, Stender S, Hardt WD, Bäumler AJ, Adams LG. 2002. The Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium effector proteins SipA, SopA, SopB, SopD, and SopE2 act in concert to induce diarrhea in calves. Infect Immun 70:3843–3855. doi:10.1128/iai.70.7.3843-3855.2002. - V体育2025版 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types (VSports在线直播)
MeSH terms (V体育ios版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
Substances
- "VSports" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

