"V体育ios版" Gut microbiota dependent anti-tumor immunity restricts melanoma growth in Rnf5-/- mice
- PMID: 30940817
- PMCID: "V体育平台登录" PMC6445090
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09525-y
Gut microbiota dependent anti-tumor immunity restricts melanoma growth in Rnf5-/- mice
Abstract (VSports app下载)
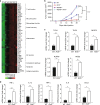
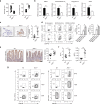
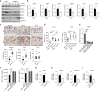
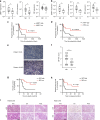
Accumulating evidence points to an important role for the gut microbiome in anti-tumor immunity. Here, we show that altered intestinal microbiota contributes to anti-tumor immunity, limiting tumor expansion. Mice lacking the ubiquitin ligase RNF5 exhibit attenuated activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) components, which coincides with increased expression of inflammasome components, recruitment and activation of dendritic cells and reduced expression of antimicrobial peptides in intestinal epithelial cells. Reduced UPR expression is also seen in murine and human melanoma tumor specimens that responded to immune checkpoint therapy. Co-housing of Rnf5-/- and WT mice abolishes the anti-tumor immunity and tumor inhibition phenotype, whereas transfer of 11 bacterial strains, including B. rodentium, enriched in Rnf5-/- mice, establishes anti-tumor immunity and restricts melanoma growth in germ-free WT mice. Altered UPR signaling, exemplified in Rnf5-/- mice, coincides with altered gut microbiota composition and anti-tumor immunity to control melanoma growth VSports手机版. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures (V体育2025版)


"V体育官网入口" References
-
- Sharma P, Allison JP. Immune checkpoint targeting in cancer therapy: toward combination strategies with curative potential. Cell. 2015;161:205–214. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.030. - DOI (VSports手机版) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sivan A, et al. Commensal Bifidobacterium promotes antitumor immunity and facilitates anti-PD-L1 efficacy. Science. 2015;350:1084–1089. doi: 10.1126/science.aac4255. - DOI (VSports最新版本) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vetizou M, et al. Anticancer immunotherapy by CTLA-4 blockade relies on the gut microbiota. Science. 2015;350:1079–1084. doi: 10.1126/science.aad1329. - DOI (VSports) - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
VSports最新版本 - Substances
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
Grants and funding
- R35CA197465 /NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI106895/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA128814/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports手机版" P30 CA030199 /NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197465/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA198103/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA216187 /NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA030199/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK113171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK103185 /NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA216187/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports在线直播" R01 CA198103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
VSports手机版 - Medical
"V体育ios版" Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

