PRMT5 enhances tumorigenicity and glycolysis in pancreatic cancer via the FBW7/cMyc axis
- PMID: 30922330
- PMCID: PMC6440122
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-019-0344-4
PRMT5 enhances tumorigenicity and glycolysis in pancreatic cancer via the FBW7/cMyc axis
Abstract
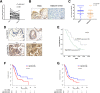
Background: The epigenetic factor protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) has been reported to play vital roles in a wide range of cellular processes, such as gene transcription, genomic organization, differentiation and cell cycle control. However, its role in pancreatic cancer remains unclear VSports手机版. Our study aimed to investigate the roles of PRMT5 in pancreatic cancer prognosis and progression and to explore the underlying molecular mechanism. .
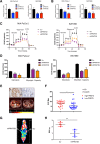
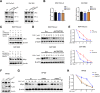
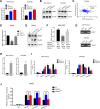
Methods: Real-time PCR, immunohistochemistry and analysis of a dataset from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) were performed to study the expression of PRMT5 at the mRNA and protein levels in pancreatic cancer. Cell proliferation assays, including cell viability, colony formation ability and subcutaneous mouse model assays, were utilized to confirm the role of PRMT5 in cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. A Seahorse extracellular flux analyzer, a glucose uptake kit, a lactate level measurement kit and the measurement of 18F-FDG (fluorodeoxyglucose) uptake by PET/CT (positron emission tomography/computed tomography) imaging were used to verify the role of PRMT5 in aerobic glycolysis, which sustains cell proliferation V体育安卓版. The regulatory effect of PRMT5 on cMyc, a master regulator of oncogenesis and aerobic glycolysis, was explored by quantitative PCR and protein stability measurements. .
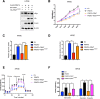
Results: PRMT5 expression was significantly upregulated in pancreatic cancer tissues compared with that in adjacent normal tissues. Clinically, elevated expression of PRMT5 was positively correlated with worse overall survival in pancreatic cancer patients. Silencing PRMT5 expression inhibited the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, PRMT5 regulated aerobic glycolysis in vitro in cell lines, in vivo in pancreatic cancer patients and in a xenograft mouse model used to measure 18F-FDG uptake. We found that mechanistically, PRMT5 posttranslationally regulated cMyc stability via F-box/WD repeat-containing protein 7 (FBW7), an E3 ubiquitin ligase that controls cMyc degradation V体育ios版. Moreover, PRMT5 epigenetically regulated the expression of FBW7 in pancreatic cancer cells. .
Conclusions: The present study demonstrated that PRMT5 epigenetically silenced the expression of the tumor suppressor FBW7, leading to increased cMyc levels and the subsequent enhancement of the proliferation of and aerobic glycolysis in pancreatic cancer cells. The PRMT5/FBW7/cMyc axis could be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of pancreatic cancer VSports最新版本. .
Keywords: Aerobic glycolysis; FBW7; PRMT5; Pancreatic cancer; cMyc V体育平台登录. .
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The research protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of FDUSCC VSports注册入口. This study complied with the Animal Care guidelines of FDUSCC.
Consent for publication
All of the authors listed consented to publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures (V体育2025版)

VSports最新版本 - References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Bosetti C, et al. Pancreatic cancer: overview of descriptive epidemiology. Mol Carcinog. 2012;51(1):3–13. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
Substances
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
V体育2025版 - Medical
"VSports在线直播" Research Materials

