Multiomic Profiling Identifies cis-Regulatory Networks Underlying Human Pancreatic β Cell Identity and Function
- PMID: 30650367
- PMCID: PMC6389269
- DOI: "V体育平台登录" 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.12.083
Multiomic Profiling Identifies cis-Regulatory Networks Underlying Human Pancreatic β Cell Identity and Function
Abstract
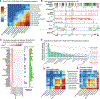
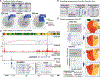
EndoC-βH1 is emerging as a critical human β cell model to study the genetic and environmental etiologies of β cell (dys)function and diabetes VSports手机版. Comprehensive knowledge of its molecular landscape is lacking, yet required, for effective use of this model. Here, we report chromosomal (spectral karyotyping), genetic (genotyping), epigenomic (ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq), chromatin interaction (Hi-C and Pol2 ChIA-PET), and transcriptomic (RNA-seq and miRNA-seq) maps of EndoC-βH1. Analyses of these maps define known (e. g. , PDX1 and ISL1) and putative (e. g. , PCSK1 and mir-375) β cell-specific transcriptional cis-regulatory networks and identify allelic effects on cis-regulatory element use. Importantly, comparison with maps generated in primary human islets and/or β cells indicates preservation of chromatin looping but also highlights chromosomal aberrations and fetal genomic signatures in EndoC-βH1. Together, these maps, and a web application we created for their exploration, provide important tools for the design of experiments to probe and manipulate the genetic programs governing β cell identity and (dys)function in diabetes. .
Keywords: (epi)genome; EndoC-βH1; Hi-C; Pol2 ChIA-PET; genetics; human pancreatic islets; karyotype; transcriptome; type 2 diabetes; β cell V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s) V体育ios版. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. .
V体育2025版 - Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Andersson LE, Valtat B, Bagge A, Sharoyko VV, Nicholls DG, Ravassard P, Scharfmann R, Spégel P, and Mulder H (2015). Characterization of stimulus-secretion coupling in the human pancreatic EndoC-βH1 β cell line. PLoS ONE 10, e0120879. - V体育ios版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blom AM (2017). The role of complement inhibitors beyond controlling inflammation. J. Intern. Med 282, 116–128. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
"VSports" MeSH terms
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (VSports app下载)
Full Text Sources (V体育平台登录)
Molecular Biology Databases

