Evidence for Viral Induction of Biliary Atresia: A Review
- PMID: 30637219
- PMCID: PMC6328731
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2018.00046
Evidence for Viral Induction of Biliary Atresia: A Review
Abstract
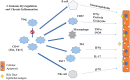
Biliary atresia (BA) is a childhood disease which manifests with abnormal narrowing, blockage or complete absence of bile ducts within the liver. Many possible etiologies have been reported for the development of BA, including congenital, perinatal and acquired conditions. Since the 1970's, there has been increasing evidence linking BA development to viral perinatal infections. The viral vectors most commonly implicated include members of the herpesviridae family (cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus) as well as those of the reoviridae family (reovirus and rotavirus) VSports手机版. While extensive work has been done on a murine model of disease, the current review focuses primarily on evidence from human studies of viral vectors in children afflicted with BA. .
Keywords: Biliary atresia; Cytomegalovirus; Epstein-Barr virus; Reovirus; Rotavirus V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures

References
-
- Harpavat S, Finegold MJ, Karpen SJ. Patients with biliary atresia have elevated direct/conjugated bilirubin levels shortly after birth. Pediatrics. 2011;128:e1428–e1433. doi: 10.1542/peds.2011-1869. - VSports手机版 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davenport M, Ure BM, Petersen C, Kobayashi H. Surgery for biliary atresia–is there a European consensus? Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2007;17:180–183. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-965147. - DOI (VSports手机版) - PubMed
"V体育平台登录" Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
