High plasma resistin associates with severe acute kidney injury in Puumala hantavirus infection
- PMID: 30517161
- PMCID: PMC6281250
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208017
High plasma resistin associates with severe acute kidney injury in Puumala hantavirus infection
Abstract
Background: Puumala hantavirus (PUUV) infected patients typically suffer from acute kidney injury (AKI) VSports手机版. Adipokines have inflammation modulating functions in acute diseases including AKI. We examined plasma levels of three adipokines (resistin, leptin, and adiponectin) in acute PUUV infection and their associations with disease severity. .
Methods: This study included 79 patients hospitalized due to acute PUUV infection. Plasma resistin, leptin, adiponectin, as well as IL-6 and CRP, were measured at the acute phase, recovery phase and one year after hospitalization V体育安卓版. .
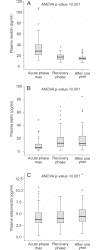
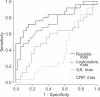
Results: Plasma resistin levels were significantly higher in the acute phase compared to the recovery phase and one year after (median resistin 28 pg/mL (11-107) vs. 17 pg/mL (7-36) vs V体育ios版. 14 pg/mL (7-31), p<0. 001). Maximum resistin concentration correlated with maximum plasma creatinine levels (r = 0. 63; p<0. 001). The higher the amount of albuminuria in the urine dipstick test (0-1+, 2+ or 3+) at admission, the higher the median of maximum resistin (24. 7 pg/mL, 25. 4 pg/mL and 39. 6 pg/mL, respectively, p = 0. 002). High resistin was also an independent risk factor for severe AKI (creatinine ≥353. 6μmol/L) (OR 1. 08, 95% CI 1. 02-1. 14). Neither plasma leptin nor adiponectin level had any correlation with creatinine concentration or the amount of albuminuria. .
Conclusions: Plasma resistin independently associates with the severity of AKI in acute PUUV infection VSports最新版本. The association of resistin with the amount of albuminuria suggests that the level of plasma resistin is not only influenced by renal clearance but could have some role in the pathogenesis of AKI during PUUV infection. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
"V体育2025版" Figures
References
-
- Vaheri A, Strandin T, Hepojoki J, Sironen T, Henttonen H, Mäkelä S, et al. Uncovering the mysteries of hantavirus infections. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013; 11(8): 539–50. - PubMed
-
- Mustonen J, Mäkelä S, Outinen T, Laine O, Jylhävä J, Arstila PT, et al. The pathogenesis of nephropathia epidemica: new knowledge and unanswered questions. Antiviral Res. 2013; 100(3): 589–604. 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.10.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Latus J, Schwab M, Tacconelli E, Pieper FM, Wegener D, Dippon J, et al. Clinical course and long-term outcome of hantavirus-associated nephropathia epidemica, Germany. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015; 21(1): 76–83. 10.3201/eid2101.140861 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Braun N, Haap M, Overkamp D, Kimmel M, Alscher MD, Lehnert H, et al. Characterization and outcome following Puumala virus infection: a retrospective analysis of 75 cases. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010; 25(9): 2997–3003. 10.1093/ndt/gfq118 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vaheri A, Henttonen H, Voutilainen L, Mustonen J, Sironen T, Vapalahti O. Hantavirus infections in Europe and their impact on public health. Rev Med Virol. 2013; 23(1): 35–49. 10.1002/rmv.1722 - DOI - PubMed
V体育官网 - Publication types
"V体育平台登录" MeSH terms
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
Substances
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
"V体育2025版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials (V体育平台登录)
Miscellaneous

