Potential therapy strategy: targeting mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis
- PMID: 30474573
- PMCID: PMC6260865
- DOI: 10.1186/s40779-018-0187-0
Potential therapy strategy: targeting mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis
V体育2025版 - Abstract
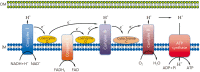
Recently, the definition of sepsis was concluded to be a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection. Severe patients always present with uncorrectable hypotension or hyperlactacidemia, which is defined as septic shock. The new definition emphasizes dysregulation of the host response and multiple organ dysfunction, which is partially attributed to metabolic disorders induced by energy crisis and oxidative stress. Mitochondria are a cellular organelle that are well known as the center of energy production, and mitochondrial damage or dysfunction is commonly induced in septic settings and is a predominant factor leading to a worse prognosis. In the present review, we determine the major mitochondrial disorders from morphology to functions in sepsis. In the following, several clinical or pre-clinical assays for monitoring mitochondrial function are demonstrated according to accumulated evidence, which is the first step of specific therapy targeting to modulate mitochondrial function. Accordingly, various reagents used for regulating mitochondrial enzyme activities and promoting biogenesis have been documented, among which mitochondria-targeted cation, TPP-conjugated antioxidants are the most valuable for future trials and clinical treatment to improve mitochondrial function as they may take advantage of the prognosis associated with septic complications. VSports手机版.
Keywords: Electron transfer chain; Mitochondria; Monitor; Sepsis; Therapy strategy. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures (VSports最新版本)
References
Publication types
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
"VSports手机版" MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports最新版本" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

