Network pharmacology-based strategy to investigate pharmacological mechanisms of Zuojinwan for treatment of gastritis
- PMID: 30382864
- PMCID: PMC6211468
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2356-9
"VSports最新版本" Network pharmacology-based strategy to investigate pharmacological mechanisms of Zuojinwan for treatment of gastritis
Abstract
Background: Zuojinwan (ZJW), a classic herbal formula, has been extensively used to treat gastric symptoms in clinical practice in China for centuries. However, the pharmacological mechanisms of ZJW still remain vague to date. VSports手机版.
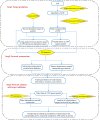
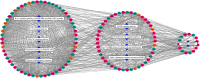
Methods: In the present work, a network pharmacology-based strategy was proposed to elucidate its underlying multi-component, multi-target, and multi-pathway mode of action against gastritis. First we collected putative targets of ZJW based on TCMSP and STITCH databases, and a network containing the interactions between the putative targets of ZJW and known therapeutic targets of gastritis was built. Then four topological parameters, "degree", "betweenness", "closeness", and "coreness" were calculated to identify the major targets in the network V体育安卓版. Furthermore, the major hubs were imported to the Metacore database to perform a pathway enrichment analysis. .
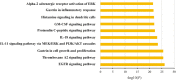
Results: A total of 118 nodes including 59 putative targets of ZJW were picked out as major hubs in terms of their topological importance. The results of pathway enrichment analysis indicated that putative targets of ZJW mostly participated in various pathways associated with anti-inflammation response, growth and development promotion and G-protein-coupled receptor signaling. More importantly, five putative targets of ZJW (EGFR, IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α and MCP-1) and two known therapeutic targets of gastritis (CCKBR and IL-12β) and a link target NF-κB were recognized as active factors involved in the main biological functions of treatment, implying the underlying mechanisms of ZJW acting on gastritis V体育ios版. .
Conclusion: ZJW could alleviate gastritis through the molecular mechanisms predicted by network pharmacology, and this research demonstrates that the network pharmacology approach can be an effective tool to reveal the mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) from a holistic perspective VSports最新版本. .
Keywords: Gastritis; Network pharmacology; Zuojinwan. V体育平台登录.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Paduraru G, Lupu VV, Diaconescu S, Burlea M. Particular considerations on helicobacter pylori-associated chronic gastritis in child. Romanian J Pediatr. 2011;60(1):29–33.
-
- Ali El Zahaby A, Abdel Alim A, Elsharawy A. Role of Rebamipide and \ or pantoprazole in preventing dexamethasone induced gastritis in senile male albino rats. Egypt J Hosp Med. 2017;67(2):789–505. doi: 10.12816/0037837. - DOI
-
- Jones L, Brooks D. Cash. Gastritis. In Digestive Disease, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/gastritis. Accessed July 2015.
-
- Rosen & Barkin's 5-Minute Emergency Medicine Consult (4 ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2015:447.
-
- Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2013,5 Books in 1, Expert Consult - Online and Print,1: Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2013. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2016:417.
VSports app下载 - MeSH terms
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
Substances
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育安卓版)
"VSports app下载" Research Materials
Miscellaneous

