Recruitment of activated neutrophils correlates with disease severity in adult Crohn's disease
- PMID: 30347439
- PMCID: PMC6330654 (VSports)
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13226 (V体育2025版)
"V体育ios版" Recruitment of activated neutrophils correlates with disease severity in adult Crohn's disease
Abstract
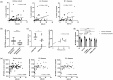
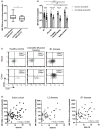
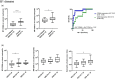
Neutrophils are detected in inflamed colon in Crohn's disease (CD) VSports手机版. However, whether the frequency and/or activation of circulating or gut tissue neutrophils correlate with endoscopic severity remains to be investigated. A cohort of 73 CD patients was prospectively enrolled according to endoscopic severity and treatment history. Individuals with active disease were stratified using the Montreal classification. Harvey-Bradshaw Index (HBI) and Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn's Disease (SES-CD) were performed at the time of ileocolonoscopy. Frequency of neutrophils and their expression of CD66b and CD64 were assessed in paired blood and colonic biopsies using flow cytometry. The percentage of neutrophils increased in inflamed colon and correlated with SES-CD in the entire cohort of patients examined, as well as in the subgroup with inflammatory (B1) active disease. SES-CD further correlated with neutrophil CD66b expression in mucosa but not blood and, conversely, with neutrophil CD64 expression in blood but not mucosa. However, the evaluation of neutrophil activation in mucosa when compared to blood reflected disease activity more clearly. Finally, a neutrophil activation power index (CD66b in mucosa X CD64 in blood) that correlated with SES-CD discriminated between patients with mild and severe disease. In conclusion, the frequency and activation of colonic neutrophils correlated with SES-CD, highlighting that mucosal neutrophils are associated with disease severity in CD. .
Keywords: CD64; CD66b; Crohn’s disease; SES-CD; neutrophil V体育安卓版. .
© 2018 British Society for Immunology.
Figures

References
-
- Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N et al Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population‐based studies. Lancet 2018;390:2769–78. - "V体育官网入口" PubMed
-
- Magro F, Langner C, Driessen A et al European consensus on the histopathology of inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis 2013;7:827–51. - "V体育ios版" PubMed
-
- Wera O, Lancellotti P, Oury C. The dual role of neutrophils in inflammatory bowel diseases. J Clin Med 2016;5:118. - PMC (V体育官网) - PubMed
-
- Lemmens B, Arijs I, Van Assche G et al Correlation between the endoscopic and histologic score in assessing the activity of ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2013;19:1194–201. - PubMed (V体育平台登录)
-
- Yoon J, Terada A, Kita H. CD66b regulates adhesion and activation of human eosinophils. J Immunol 2007;179:8454–62. - PubMed
V体育官网入口 - Publication types
- VSports app下载 - Actions
MeSH terms
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Substances
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports在线直播" Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

