"V体育平台登录" How Lipid-Specific T Cells Become Effectors: The Differentiation of iNKT Subsets
- PMID: 29997620
- PMCID: PMC6028555
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01450
How Lipid-Specific T Cells Become Effectors: The Differentiation of iNKT Subsets
"V体育ios版" Abstract
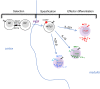
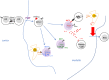
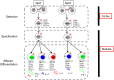
In contrast to peptide-recognizing T cells, invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells express a semi-invariant T cell receptor that specifically recognizes self- or foreign-lipids presented by CD1d molecules. There are three major functionally distinct effector states for iNKT cells. Owning to these innate-like effector states, iNKT cells have been implicated in early protective immunity against pathogens. Yet, growing evidence suggests that iNKT cells play a role in tissue homeostasis as well. In this review, we discuss current knowledge about the underlying mechanisms that regulate the effector states of iNKT subsets, with a highlight on the roles of a variety of transcription factors and describe how each subset influences different facets of thymus homeostasis. VSports手机版.
Keywords: development; invariant natural killer T cell; lipid; mucosal-associated invariant T cell; subsets; thymus V体育安卓版. .
Figures
References
-
- Ohteki T, MacDonald HR. Major histocompatibility complex class I related molecules control the development of CD4+8- and CD4-8- subsets of natural killer 1.1+ T cell receptor-alpha/beta+ cells in the liver of mice. J Exp Med (1994) 180(2):699–704.10.1084/jem.180.2.699 - "VSports" DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Egawa T, Eberl G, Taniuchi I, Benlagha K, Geissmann F, Hennighausen L, et al. Genetic evidence supporting selection of the Valpha14i NKT cell lineage from double-positive thymocyte precursors. Immunity (2005) 22(6):705–16.10.1016/j.immuni.2005.03.011 - DOI (VSports注册入口) - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
"VSports最新版本" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

