Regulatory γδ T cells induced by G-CSF participate in acute graft-versus-host disease regulation in G-CSF-mobilized allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 29801459
- PMCID: PMC5970446
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-018-1519-2 (V体育官网)
Regulatory γδ T cells induced by G-CSF participate in acute graft-versus-host disease regulation in G-CSF-mobilized allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation
Abstract
Background: The immunomodulatory effects of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) on T cells result in a low incidence of acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) in G-CSF-mobilized allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (G-PBSCT). However, the exact mechanism remains unclear. Regulatory γδ T cells (γδTregs), characterized by the presence of TCRγδ and Foxp3, have aroused great concern in the maintenance of immune tolerance. We hypothesized that γδTregs might involve in the immunomodulatory effects of G-CSF mobilization. VSports手机版.
Methods: The expression and immunomodulatory function of γδTreg subsets in peripheral blood of donors before and after G-CSF treatment in vivo and in vitro were evaluated by flow cytometry and CFSE assays. To investigate the effects of γδTregs on aGVHD, the association between γδTreg subsets in grafts and aGVHD in recipients was estimated. V体育安卓版.
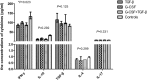
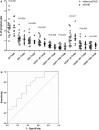
Results: The proportions of Vδ1Tregs, CD27+Vδ1Tregs and CD25+Vδ1Tregs were significantly increased in peripheral blood after G-CSF treatment in vivo. γδTregs could be generated in vitro by stimulating with anti-TCRγδ in the presence of G-CSF. The immune phenotype, proliferation suppression function, and cytokine secretion of G-CSF-induced γδTregs were similar to that of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-induced γδTregs. The clinical data demonstrated that the proportion of CD27+Vδ1Tregs in grafts was significantly lower in the patients who experienced aGVHD than in those who did not develop aGVHD (P = 0. 028), and the proportions of other γδTreg subsets in grafts did not differ significantly between the two groups. The best cutoff value for CD27+Vδ1Treg proportion in grafts in prediction of aGVHD was 0. 33%, with an area under the curve value of 0. 725 (P = 0. 043). Eight patients (26. 7%) were classified as the low-CD27+Vδ1Treg group (< 0. 33%), and 22 patients (73. 3%) as the high-CD27+Vδ1Treg group (≥ 0. 33%). The incidence of aGVHD was higher in the low-CD27+Vδ1Treg group than in the high-CD27+Vδ1Treg group (75 V体育ios版. 0% versus 22. 7%, P = 0. 028). .
Conclusions: G-CSF could induce the generation of γδTregs in vivo and in vitro, and γδTregs might participate in aGVHD regulation in G-PBSCT. VSports最新版本.
Keywords: Acute graft-versus-host disease; Allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation; Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; Regulatory γδ T cells V体育平台登录. .
Figures






"VSports最新版本" References
-
- Nagler A, Labopin M, Shimoni A, Mufti GJ, Cornelissen JJ, Blaise D, et al. Mobilized peripheral blood stem cells compared with bone marrow from HLA-identical siblings for reduced-intensity conditioning transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia in complete remission: a retrospective analysis from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of EBMT. Eur J Haematol. 2012;89:206–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.2012.01811.x. - DOI (VSports app下载) - PubMed
-
- Arpinati M, Green CL, Heimfeld S, Heuser JE, Anasetti C. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor mobilizes T helper 2-inducing dendritic cells. Blood. 2000;95:2484–2490. - "V体育2025版" PubMed
VSports手机版 - Publication types
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
Substances
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
Grants and funding
- No. 81770150/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- No. 81300445/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- No. 81401315/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- No. 81270647/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- No. 81200388/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International (VSports)
- "V体育平台登录" No. 81470349/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- No. 81000231/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- No. U1401221/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- No.2015J003/Outstanding Youths Development Scheme of Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University/International
- No. 2014A030310171/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province/International
- No. S2012010009299/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province/International
- "V体育ios版" No. 2014A030313380/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province/International
- No.201806010029/Project of the Zhujiang Science & Technology Star of Guangzhou City/International
- No. 2013J2200046/Project of the Zhujiang Science & Technology Star of Guangzhou City/International
- No. 21617465/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities/International (V体育2025版)
LinkOut - more resources (V体育2025版)
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

