Delayed immune reconstitution after allogeneic transplantation increases the risks of mortality and chronic GVHD (V体育2025版)
- PMID: 29678809
- PMCID: PMC5916001
- DOI: VSports手机版 - 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017014464
Delayed immune reconstitution after allogeneic transplantation increases the risks of mortality and chronic GVHD (V体育2025版)
Abstract
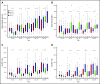
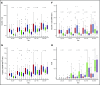
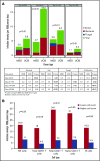
Slow immune reconstitution is a major obstacle to the successful use of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT). As matched sibling donor (MSD) allo-HCT is regarded as the gold standard, we evaluated the pace of immune reconstitution in 157 adult recipients of reduced-intensity conditioning followed by MSD peripheral blood HCT (n = 68) and compared these to recipients of umbilical cord blood (UCB; n = 89). At day 28, UCB recipients had fewer natural killer (NK) cells than MSD recipients, but thereafter, NK cell numbers (and their subsets) were higher in UCB recipients. During the first 6 months to 1 year after transplant, UCB recipients had slower T-cell subset recovery, with lower numbers of CD3+, CD8+, CD8+ naive, CD4+ naive, CD4+ effector memory T, regulatory T, and CD3+CD56+ T cells than MSD recipients. Notably, B-cell numbers were higher in UCB recipients from day 60 to 1 year. Bacterial and viral infections were more frequent in UCB recipients, yet donor type had no influence on treatment-related mortality or survival. Considering all patients at day 28, lower numbers of total CD4+ T cells and naive CD4+ T cells were significantly associated with increased infection risk, treatment-related mortality, and chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) VSports手机版. Patients with these characteristics may benefit from enhanced or prolonged infection surveillance and prophylaxis as well as immune reconstitution-accelerating strategies. .
© 2018 by The American Society of Hematology V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Parody R, Martino R, Rovira M, et al. . Severe infections after unrelated donor allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adults: comparison of cord blood transplantation with peripheral blood and bone marrow transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006;12(7):734-748. - PubMed
-
- Komanduri KV, St John LS, de Lima M, et al. . Delayed immune reconstitution after cord blood transplantation is characterized by impaired thymopoiesis and late memory T-cell skewing. Blood. 2007;110(13):4543-4551. - V体育安卓版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ruggeri A, Peffault de Latour R, Carmagnat M, et al. . Outcomes, infections, and immune reconstitution after double cord blood transplantation in patients with high-risk hematological diseases. Transpl Infect Dis. 2011;13(5):456-465. - PubMed (V体育官网)
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
Grants and funding
V体育官网 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育ios版" Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

