VSports app下载 - Lymphocyte subset expression and serum concentrations of PD-1/PD-L1 in sepsis - pilot study
- PMID: 29661225
- PMCID: PMC5902875
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-018-2020-2
"VSports在线直播" Lymphocyte subset expression and serum concentrations of PD-1/PD-L1 in sepsis - pilot study
Abstract
Background: Sepsis remains a major cause of mortality in critical care, for which specific treatments are lacking. The dysregulated response to infection seen in sepsis includes features of lymphocyte dysfunction and exhaustion, suggesting that immune-stimulatory therapy may improve outcomes in certain patient groups VSports手机版. Monoclonal antibodies targeting checkpoint molecules, such as programmed-death 1 protein (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1, have shown success in stimulating the immune response in patients with cancer, and are being considered for future sepsis trials. The aims of this pilot study were to compare lymphocyte subset expression of PD-1 and its ligands between patients with sepsis and controls; to characterize serum levels of PD-1 and PD-L1 in patients with sepsis and controls, and determine if serum concentrations correlated with cell surface expression. .
Methods: Expression levels of PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 on four lymphocyte subsets (CD27 + CD19+ B cells, CD27-CD19+ B cells, CD27 + CD4+ T cells and CD27-CD4+ T cells) were compared between 22 patients with sepsis (including 11 survivors and 11 non-survivors) and 11 healthy controls using flow cytometry V体育安卓版. Levels of soluble PD-1 and PD-L1 were also compared using commercially available ELISA kits. .
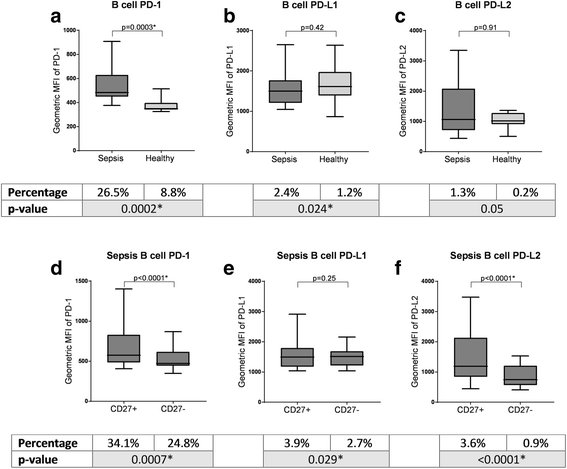
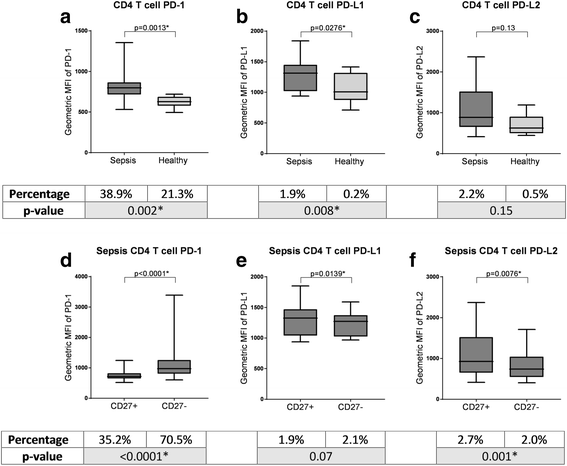
Results: Expression of PD-1 and PD-L1 was higher on all lymphocyte subsets in patients with sepsis compared to controls (p < 0. 05) V体育ios版. PD-L2 expression on CD27+ B cells was also higher in patients with sepsis (p = 0. 0317). There was differential expression of PD-1 by CD27 status, with expression being higher in the B and T cell subsets associated with memory status (CD27+ and CD27-, respectively; p < 0. 001). Higher PD-1 and PD-L1 expression was not associated with mortality or with a higher risk of nosocomial infection. There were no differences in levels of soluble PD-1 or PD-L1 between patients with sepsis and controls. .
Conclusions: Higher expression of PD-1 by memory subpopulations of B cells and CD4+ T cells, with normal soluble PD-1 and PD-L1 in patients with sepsis, are novel findings. This information may be useful to enrich sepsis populations for trials of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade. VSports最新版本.
Keywords: Enrichment; Outcomes; Programmed death-1; Sepsis; Septic shock. V体育平台登录.
"VSports app下载" Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All patients who met the eligibility criteria were consented prior to blood sampling VSports注册入口. Ethics approval for the study was given by HRA Research Ethics Committee London (Camberwell St Giles) Address: East of England REC Centre Victoria House, Capital Park Fulbourn, Cambridge CB21 5XB. Approval reference: 12/LO/0326.
Competing interests
MS is on the steering committee for a clinical trial of anti PD-L1 therapy in sepsis V体育官网入口. The other authors have no competing interests to declare.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References (VSports)
-
- Hotchkiss RS, Monneret G, Payen D. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: from cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(12):862–874. doi: 10.1038/nri3552. - V体育2025版 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scicluna BP, van Vught LA, Zwinderman AH, Wiewel MA, Davenport EE, Burnham KL, Nurnberg P, Schultz MJ, Horn J, Cremer OL, et al. Classification of patients with sepsis according to blood genomic endotype: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5(10):816–26. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30294-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chang K, Svabek C, Vazquez-Guillamet C, Sato B, Rasche D, Wilson S, Robbins P, Ulbrandt N, Suzich J, Green J, et al. Targeting the programmed cell death 1: programmed cell death ligand 1 pathway reverses T cell exhaustion in patients with sepsis. Crit Care. 2014;18(1):R3. doi: 10.1186/cc13176. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
Substances
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
"VSports app下载" Grants and funding
- VSports最新版本 - Senior Investigator Award/National Institute for Health Research
- EME/16/33/01/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- NIHR-CS-2016-16-011/National Institute for Health Research (V体育平台登录)
- ACF-2016-17-018/National Institute for Health Research
- 16/33/01/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
"V体育ios版" LinkOut - more resources
"VSports注册入口" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
"VSports最新版本" Research Materials

