Deficiency of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase in bile acid synthesis exacerbates alcohol-induced liver injury in mice
- PMID: 29404516
- PMCID: PMC5776875
- DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1129
Deficiency of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase in bile acid synthesis exacerbates alcohol-induced liver injury in mice
VSports - Abstract
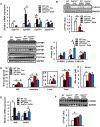
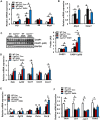
Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) is a major risk factor for cirrhosis-associated liver diseases. Studies demonstrate that alcohol increases serum bile acids in humans and rodents. AFLD has been linked to cholestasis, although the physiologic relevance of increased bile acids in AFLD and the underlying mechanism of increasing the bile acid pool by alcohol feeding are still unclear. In this study, we used mouse models either deficient of or overexpressing cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (Cyp7a1), the rate-limiting and key regulatory enzyme in bile acid synthesis, to study the effect of alcohol drinking in liver metabolism and inflammation VSports手机版. Mice were challenged with chronic ethanol feeding (10 days) plus a binge dose of alcohol by oral gavage (5 g/kg body weight). Alcohol feeding reduced bile acid synthesis gene expression but increased the bile acid pool size, hepatic triglycerides and cholesterol, and inflammation and injury in wild-type mice and aggravated liver inflammation and injury in Cyp7a1-deficient mice. Interestingly, alcohol-induced hepatic inflammation and injury were ameliorated in Cyp7a1 transgenic mice. Conclusion: Alcohol feeding alters hepatic bile acid and cholesterol metabolism to cause liver inflammation and injury, while maintenance of bile acid and cholesterol homeostasis protect against alcohol-induced hepatic inflammation and injury. Our findings indicate that CYP7A1 plays a key role in protection against alcohol-induced steatohepatitis. (Hepatology Communications 2018;2:99-112). .
Figures




VSports在线直播 - References
-
- Gao B, Bataller R. Alcoholic liver disease: pathogenesis and new therapeutic targets. Gastroenterology 2011;141:1572‐1585. - "V体育平台登录" PMC - PubMed
-
- Rehm J, Mathers C, Popova S, Thavorncharoensap M, Teerawattananon Y, Patra J. Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol‐use disorders. Lancet 2009;373:2223‐2233. - PubMed
-
- O'Shea RS, Dasarathy S, McCullough AJ; Practice Guideline Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology . Alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2010;51:307‐328. - PubMed
-
- Glover SC, McPhie JL, Brunt PW. Cholestasis in acute alcoholic liver disease. Lancet 1977;2:1305‐1307. - "VSports" PubMed
-
- Tung BY, Carithers RL Jr. Cholestasis and alcoholic liver disease. Clin Liver Dis 1999;3:585‐601. - PubMed
Grants and funding
"VSports最新版本" LinkOut - more resources
"V体育2025版" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

