Validation of Neutrophil CD64 Blood Biomarkers to Detect Mucosal Inflammation in Pediatric Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 29272485
- PMCID: PMC5831176 (V体育官网入口)
- DOI: 10.1093/ibd/izx022 (V体育ios版)
Validation of Neutrophil CD64 Blood Biomarkers to Detect Mucosal Inflammation in Pediatric Crohn's Disease
Abstract
Background: In a pilot study, neutrophil CD64 surface expression was significantly elevated in newly diagnosed, pediatric-onset Crohn's disease. We aimed to test the CD64 biomarkers (neutrophil CD64 surface expression and soluble CD64) as determinates for mucosal inflammation in a larger pediatric Crohn's cohort with the hypotheses that the CD64 biomarkers would reliably detect intestinal inflammation and correlate with endoscopic severity scores VSports手机版. .
Methods: We enrolled patients referred for colonoscopy for either suspected inflammatory bowel disease or with established Crohn's. Neutrophil CD64 index was determined by flow cytometry using a commercial kit (Leuko64, Trillium) and soluble CD64 by ELISA (LifeSpan) V体育安卓版. .
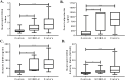
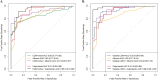
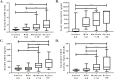
Results: A total of 209 patients (72 controls, 76 new inflammatory bowel disease patients, and 61 established Crohn's) were enrolled. Both neutrophil CD64 index and soluble CD64 were significantly elevated in new Crohn's compared with controls. The area under the curve (AUC) for neutrophil CD64 index ≥1 was 0. 85 (95% confidence interval, 0 V体育ios版. 77-0. 92), 75% sensitive and 89% specific for new Crohn's. Comparatively, soluble CD64 ≥39 ng/mL was 92% sensitive and 85% specific (AUC, 0. 93) for new Crohn's. Neutrophil CD64 index, soluble CD64, and fecal calprotectin discriminated endoscopic inactive from moderate and severe activity while soluble CD64 differentiated endoscopic mild from moderate and severe activity. Neutrophil CD64 index (r = 0. 46, P < 0. 001) and fecal calprotectin (r = 0. 55, P < 0. 001) correlated well with the Simple Endoscopic Score-Crohn's disease. Spearman correlation between the CD64 index and calprotectin was 0. 39 (P < 0. 001). .
Conclusions: In a large Crohn's disease cohort, we found that neutrophil CD64 index and soluble CD64 were significantly elevated during active gastrointestinal inflammation. VSports最新版本.
Keywords: CD64 biomarker; Crohn’s disease; pediatrics V体育平台登录. .
© 2017 Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation of America. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@qiuluzeuv.cn VSports注册入口.
Figures

References
-
- Colombel JF, Reinisch W, Mantzaris GJ et al. . Randomised clinical trial: deep remission in biologic and immunomodulator naïve patients with Crohn’s disease - a sonic post hoc analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41:734–746. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
-
- Schnitzler F, Fidder H, Ferrante M et al. . Mucosal healing predicts long-term outcome of maintenance therapy with infliximab in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009;15:1295–1301. - PubMed
VSports手机版 - Publication types
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育官网)
V体育官网 - Supplementary concepts
- VSports - Actions
Grants and funding
"V体育官网" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

