Specific oxygenation of plasma membrane phospholipids by Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipoxygenase induces structural and functional alterations in mammalian cells
- PMID: 29146531
- PMCID: PMC5764228 (V体育官网入口)
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.11.005
Specific oxygenation of plasma membrane phospholipids by Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipoxygenase induces structural and functional alterations in mammalian cells
Erratum in (VSports在线直播)
-
Corrigendum to "Specific oxygenation of plasma membrane phospholipids by Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipoxygenase induces structural and functional alterations in mammalian cells" [BBA-Mol. Cell Biol. Volume 1863/2, Pages 152-164].Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020 Aug;1865(8):158701. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158701. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020. PMID: 32354679 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
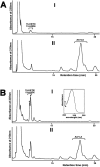
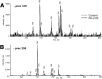
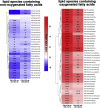
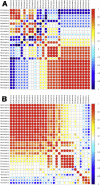
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a gram-negative pathogen, which causes life-threatening infections in immunocompromized patients. These bacteria express a secreted lipoxygenase (PA-LOX), which oxygenates free arachidonic acid to 15S-hydro(pero)xyeicosatetraenoic acid. It binds phospholipids at its active site and physically interacts with lipid vesicles. When incubated with red blood cells membrane lipids are oxidized and hemolysis is induced but the structures of the oxygenated membrane lipids have not been determined. Using a lipidomic approach, we analyzed the formation of oxidized phospholipids generated during the in vitro incubation of recombinant PA-LOX with human erythrocytes and cultured human lung epithelial cells. Precursor scanning of lipid extracts prepared from these cells followed by multiple reaction monitoring and MS/MS analysis revealed a complex mixture of oxidation products. For human red blood cells this mixture comprised forty different phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine species carrying oxidized fatty acid residues, such as hydroxy-octadecadienoic acids, hydroxy- and keto-eicosatetraenoic acid, hydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid as well as oxygenated derivatives of less frequently occurring polyenoic fatty acids VSports手机版. Similar oxygenation products were also detected when cultured lung epithelial cells were employed but here the amounts of oxygenated lipids were smaller and under identical experimental conditions we did not detect major signs of cell lysis. However, live imaging indicated an impaired capacity for trypan blue exclusion and an augmented mitosis rate. Taken together these data indicate that PA-LOX can oxidize the membrane lipids of eukaryotic cells and that the functional consequences of this reaction strongly depend on the cell type. .
Keywords: Biomembranes; Eicosanoids; Fatty acids; Infectious diseases; Lipidomics; Oxidative stress; Phospholipids V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B V体育ios版. V. All rights reserved. .
Figures





References (VSports注册入口)
-
- Andreou A., Brodhun F., Feussner I. Biosynthesis of oxylipins in non-mammals. Prog. Lipid Res. 2009;48:148–170. - PubMed
-
- Haeggstrom J.Z., Funk C.D. Lipoxygenase and leukotriene pathways: biochemistry, biology, and roles in disease. Chem. Rev. 2011;111:5866–5898. - PubMed
-
- de Bentzmann S., Plesiat P. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa opportunistic pathogen and human infections. Environ. Microbiol. 2011;13:1655–1665. - PubMed (VSports手机版)
Publication types
- "VSports" Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Substances
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
"VSports" Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

