Schrödinger's microbes: Tools for distinguishing the living from the dead in microbial ecosystems
- PMID: 28810907
- PMCID: PMC5558654
- DOI: "V体育2025版" 10.1186/s40168-017-0285-3
V体育官网 - Schrödinger's microbes: Tools for distinguishing the living from the dead in microbial ecosystems
Abstract
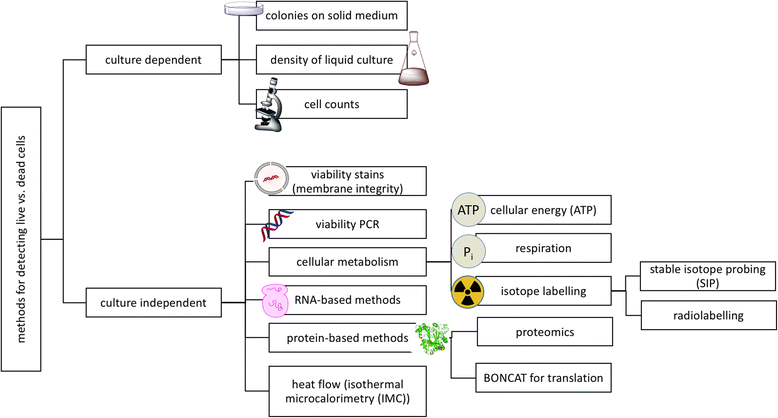
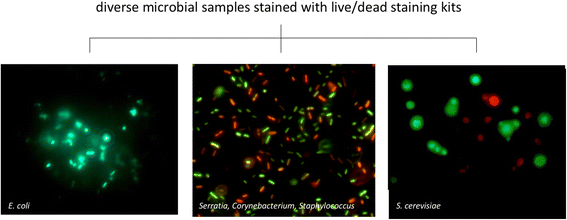
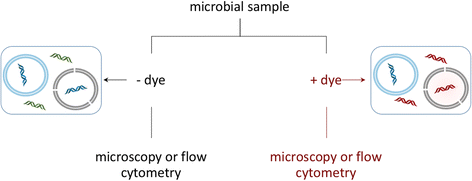
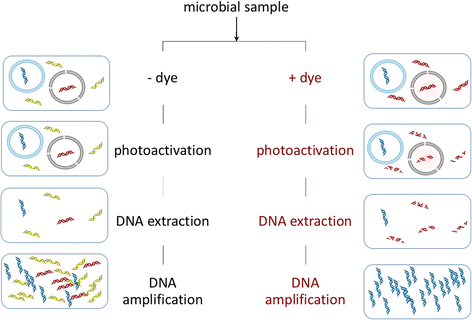
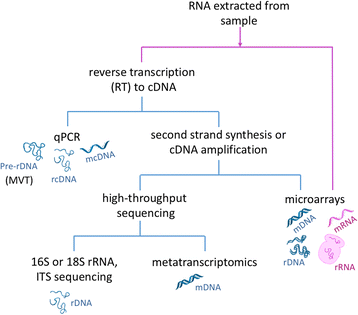
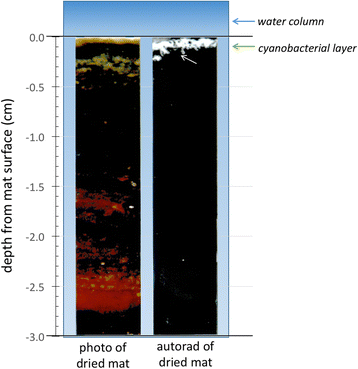
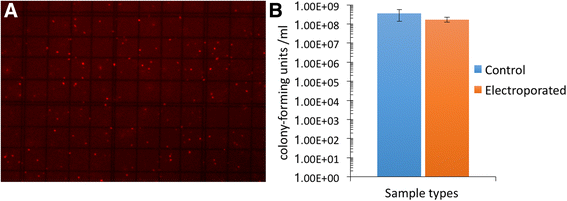
While often obvious for macroscopic organisms, determining whether a microbe is dead or alive is fraught with complications. Fields such as microbial ecology, environmental health, and medical microbiology each determine how best to assess which members of the microbial community are alive, according to their respective scientific and/or regulatory needs. Many of these fields have gone from studying communities on a bulk level to the fine-scale resolution of microbial populations within consortia. For example, advances in nucleic acid sequencing technologies and downstream bioinformatic analyses have allowed for high-resolution insight into microbial community composition and metabolic potential, yet we know very little about whether such community DNA sequences represent viable microorganisms. In this review, we describe a number of techniques, from microscopy- to molecular-based, that have been used to test for viability (live/dead determination) and/or activity in various contexts, including newer techniques that are compatible with or complementary to downstream nucleic acid sequencing VSports手机版. We describe the compatibility of these viability assessments with high-throughput quantification techniques, including flow cytometry and quantitative PCR (qPCR). Although bacterial viability-linked community characterizations are now feasible in many environments and thus are the focus of this critical review, further methods development is needed for complex environmental samples and to more fully capture the diversity of microbes (e. g. , eukaryotic microbes and viruses) and metabolic states (e. g. , spores) of microbes in natural environments. .
Keywords: DNA sequencing; Flow cytometry; Infectivity; Live/dead; Low biomass; Metagenomics; Microbial ecology; PMA; RNA; Viability; qPCR. V体育安卓版.
Figures
References
-
- Koch R. Über di neuen Untersuchungsmethoden zum Nachweis der Mikrokosmen in Boden, Luft und Wasser. Vortrag auf dem XI Deutschen Arztetag in Berlin, Vereinsblatt für Deutschland, Komnussions-Verlag von FCW Vogel, Leipzig. 1883; 137:274–84.
-
- Committee on the Forward Contamination of Mars. Preventing the forward contamination of Mars. vol ISBN: 0-309-65262-1. Division on Engineering and Physical Sciences. Washington, DC: National Research Council; 2006.
-
- Guarnieri V, Gaia E, Battocchio L, Pitzurra M, Savino A, Pasquarella C, et al. New methods for microbial contamination monitoring: an experiment on board the MIR orbital station. Acta Astronaut. 1997;40(2-8):195–201. - "V体育2025版" PubMed
-
- Koster W, Egli T, Ashbolt N, Botzenhart K, Burlion N, Endo T et al. Analytical methods for microbiological water quality testing. In: Dufour A, Snozzi M, Koster W, Bartram J, Ronchi E, Fewtrell L, editor. Microbial safety of drinking water: Improving approaches and methods. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2003. p. 237-92.
Publication types
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
LinkOut - more resources
VSports - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

