MLN4924 (Pevonedistat), a protein neddylation inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and migration of human clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 28717191
- PMCID: PMC5514088
- DOI: V体育安卓版 - 10.1038/s41598-017-06098-y
VSports最新版本 - MLN4924 (Pevonedistat), a protein neddylation inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and migration of human clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
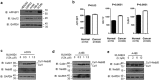
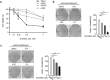
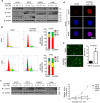
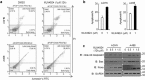
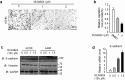
Neddylation is a post-translational protein modification associated with cancer development. MLN4924 is a neddylation inhibitor currently under investigation in multiple phase I studies on various malignancies, and its clincal name is Pevonedistat. It has been documented that MLN4924 blocks Cullins neddylation and inactivates CRLs and, in turn, triggers cell-cycle arrest, apoptosis, senescence and autophagy in many cancer cells. In this study, we investigated the anti-tumor effect of MLN4924 in human clear cell renal carcinoma (ccRCC). Levels of both Nedd8 activating enzyme E1 and Nedd8-conjugating enzyme E2 were higher in ccRCC tissues and RCC cancer cells than in normal. Moreover, MLN4924 treatment led to rapid inhibition of Cullin1 neddylation and notably suppressed growth and survival as well as migration in a dose-and time-dependent manner. Mechanistic studies revealed that MLN4924 induced the accumulation of a number of CRL substrates, including p21, p27 and Wee1 to trigger DNA damage and induce growth arrest at the G2/M phase. MLN4924 also induced anti-migration and anti-invasion by activating E-cadherin and repressing Vimentin. Taken together, this study provides the first evidence that neddylation pathway is overactive in ccRCC and that MLN4924 induces dose-dependent anti-proliferation, anti-migration, anti-invasion in ccRCC cells. The study thus indicates that MLN4924 has potential therapeutic value for the clinical treatment of renal cancer VSports手机版. .
VSports手机版 - Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer sociey. Cancer Facts & Figures 2015,. Special Se, 26, www.cancer.org (VSports注册入口).
-
- Heng DY, Choueiri TK. Non-clear cell renal cancer: features and medical management. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network: JNCCN. 2009;7:659–665. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2009.0046. - V体育安卓版 - DOI - PubMed
"VSports最新版本" Publication types
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
MeSH terms
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Substances
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
LinkOut - more resources (VSports最新版本)
"V体育2025版" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (VSports在线直播)
Medical
Miscellaneous

