CD70, a novel target of CAR T-cell therapy for gliomas
- PMID: 28651374
- PMCID: PMC5761579 (VSports手机版)
- DOI: "VSports app下载" 10.1093/neuonc/nox116
CD70, a novel target of CAR T-cell therapy for gliomas
"VSports最新版本" Abstract
Background: Cancer immunotherapy represents a promising treatment approach for malignant gliomas but is hampered by the limited number of ubiquitously expressed tumor antigens and the profoundly immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. We identified cluster of differentiation (CD)70 as a novel immunosuppressive ligand and glioma target. VSports手机版.
Methods: Normal tissues derived from 52 different organs and primary and recurrent low-grade gliomas (LGGs) and glioblastomas (GBMs) were thoroughly evaluated for CD70 gene and protein expression. The association between CD70 and patients' overall survival and its impact on T-cell death was also evaluated V体育安卓版. Human and mouse CD70-specific chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) were tested respectively against human primary GBMs and murine glioma lines. The antitumor efficacies of these CARs were also examined in orthotopic xenograft and syngeneic models. .
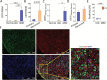
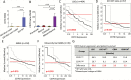
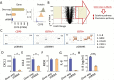
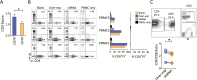
Results: CD70 was not detected in peripheral and brain normal tissues but was constitutively overexpressed by isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) wild-type primary LGGs and GBMs in the mesenchymal subgroup and recurrent tumors. CD70 was also associated with poor survival in these subgroups, which may link to its direct involvement in glioma chemokine productions and selective induction of CD8+ T-cell death. To explore the potential for therapeutic targeting of this newly identified immunosuppressive axis in GBM tumors, we demonstrate that both human and mouse CD70-specific CAR T cells recognize primary CD70+ GBM tumors in vitro and mediate the regression of established GBM in xenograft and syngeneic models without illicit effect. V体育ios版.
Conclusion: These studies identify a previously uncharacterized and ubiquitously expressed immunosuppressive ligand CD70 in GBMs that also holds potential for serving as a novel CAR target for cancer immunotherapy in gliomas VSports最新版本. .
Keywords: CD70; chimeric antigen receptors (CARs); gliomas; immunosuppressive ligand; immunotherapy. V体育平台登录.
© The Author(s) 2017 VSports注册入口. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@qiuluzeuv.cn .
VSports app下载 - Figures

"V体育官网" References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP et al. . Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10(5):459–466. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ et al. ; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987–996. - PubMed
-
- Mellman I, Coukos G, Dranoff G. Cancer immunotherapy comes of age. Nature. 2011;480(7378):480–489. - PMC (V体育安卓版) - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg SA, Restifo NP, Yang JC, Morgan RA, Dudley ME. Adoptive cell transfer: a clinical path to effective cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8(4):299–308. - "V体育安卓版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Morgan RA, Johnson LA, Davis JL et al. . Recognition of glioma stem cells by genetically modified T cells targeting EGFRvIII and development of adoptive cell therapy for glioma. Hum Gene Ther. 2012;23(10):1043–1053. - "VSports手机版" PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育ios版" Actions
V体育ios版 - MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Substances
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育官网入口" Other Literature Sources
"V体育官网" Medical
Research Materials

