GATA3 targets semaphorin 3B in mammary epithelial cells to suppress breast cancer progression and metastasis
- PMID: 28581515
- PMCID: PMC5629104
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2017.165
GATA3 targets semaphorin 3B in mammary epithelial cells to suppress breast cancer progression and metastasis
Abstract
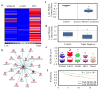
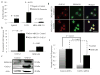
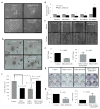
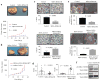
Semaphorin 3B (SEMA3B) is a secreted axonal guidance molecule that is expressed during development and throughout adulthood. Recently, SEMA3B has emerged as a tumor suppressor in non-neuronal cells. Here, we show that SEMA3B is a direct target of GATA3 transcriptional activity. GATA3 is a key transcription factor that regulates genes involved in mammary luminal cell differentiation and tumor suppression. We show that GATA3 relies on SEMA3B for suppression of tumor growth. Loss of SEMA3B renders GATA3 inactive and promotes aggressive breast cancer development. Overexpression of SEMA3B in cells lacking GATA3 induces a GATA3-like phenotype and higher levels of SEMA3B are associated with better cancer patient prognosis VSports手机版. Moreover, SEMA3B interferes with activation of LIM kinases (LIMK1 and LIMK2) to abrogate breast cancer progression. Our data provide new insights into the role of SEMA3B in mammary gland and provides a new branch of GATA3 signaling that is pivotal for inhibition of breast cancer progression and metastasis. .
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Luo Y, Raible D, Raper JA. Collapsin: a protein in brain that induces the collapse and paralysis of neuronal growth cones. Cell. 1993;75(2):217–27. - PubMed
-
- Neufeld G, Kessler O. The semaphorins: versatile regulators of tumour progression and tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8(8):632–45. - "VSports在线直播" PubMed
-
- Staton CA, Shaw LA, Valluru M, Hoh L, Koay I, Cross SS, et al. Expression of class 3 semaphorins and their receptors in human breast neoplasia. Histopathology. 2011;59(2):274–82. - PubMed
-
- Kruger RP, Aurandt J, Guan KL. Semaphorins command cells to move. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6(10):789–800. - PubMed
-
- Driessens MH, Hu H, Nobes CD, Self A, Jordens I, Goodman CS, et al. Plexin-B semaphorin receptors interact directly with active Rac and regulate the actin cytoskeleton by activating Rho. Curr Biol. 2001;11(5):339–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
Substances
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
VSports最新版本 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports注册入口" Other Literature Sources
"V体育官网入口" Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

