Bromodomain Protein BRD4 Is a Transcriptional Repressor of Autophagy and Lysosomal Function
- PMID: 28525743
- PMCID: PMC5446411
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.04.027
Bromodomain Protein BRD4 Is a Transcriptional Repressor of Autophagy and Lysosomal Function
Abstract
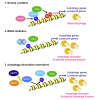
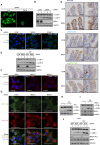
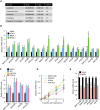
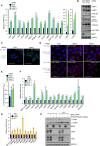
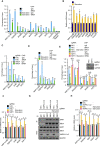
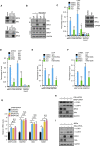
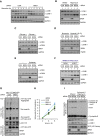
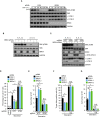
Autophagy is a membrane-trafficking process that directs degradation of cytoplasmic material in lysosomes. The process promotes cellular fidelity, and while the core machinery of autophagy is known, the mechanisms that promote and sustain autophagy are less well defined. Here we report that the epigenetic reader BRD4 and the methyltransferase G9a repress a TFEB/TFE3/MITF-independent transcriptional program that promotes autophagy and lysosome biogenesis. We show that BRD4 knockdown induces autophagy in vitro and in vivo in response to some, but not all, situations. In the case of starvation, a signaling cascade involving AMPK and histone deacetylase SIRT1 displaces chromatin-bound BRD4, instigating autophagy gene activation and cell survival. Importantly, this program is directed independently and also reciprocally to the growth-promoting properties of BRD4 and is potently repressed by BRD4-NUT, a driver of NUT midline carcinoma. These findings therefore identify a distinct and selective mechanism of autophagy regulation VSports手机版. .
Keywords: AMPK; BRD4; BRD4-NUT; G9a/EHMT2/KMT1C; SIRT1; autophagy; hMOF/KAT8; lysosomes; selective autophagy; transcriptional regulation of autophagy V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2017 The Authors V体育ios版. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. .
VSports最新版本 - Figures
Comment in
-
BRD4 is a newly characterized transcriptional regulator that represses autophagy and lysosomal function.Autophagy. 2017;13(11):1801-1803. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1364334. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Autophagy. 2017. PMID: 28837371 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baek S.H., Kim K.I. Epigenetic control of autophagy: nuclear events gain more attention. Mol. Cell. 2017;65:781–785. - PubMed
-
- Bauer P.O., Goswami A., Wong H.K., Okuno M., Kurosawa M., Yamada M., Miyazaki H., Matsumoto G., Kino Y., Nagai Y., Nukina N. Harnessing chaperone-mediated autophagy for the selective degradation of mutant huntingtin protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010;28:256–263. - V体育ios版 - PubMed
V体育官网 - MeSH terms
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
Substances
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (VSports最新版本)
"V体育官网" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
"VSports注册入口" Molecular Biology Databases
"VSports" Research Materials
Miscellaneous

