A Network-Based Pharmacology Study of the Herb-Induced Liver Injury Potential of Traditional Hepatoprotective Chinese Herbal Medicines
- PMID: 28420096
- PMCID: V体育官网入口 - PMC6154655
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22040632 (V体育平台登录)
A Network-Based Pharmacology Study of the Herb-Induced Liver Injury Potential of Traditional Hepatoprotective Chinese Herbal Medicines
Abstract
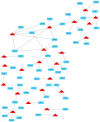
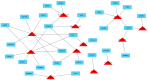
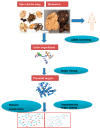
Herbal medicines are widely used for treating liver diseases and generally regarded as safe due to their extensive use in Traditional Chinese Medicine practice for thousands of years. However, in recent years, there have been increased concerns regarding the long-term risk of Herb-Induced Liver Injury (HILI) in patients with liver dysfunction. Herein, two representative Chinese herbal medicines: one-Xiao-Chai-Hu-Tang (XCHT)-a composite formula, and the other-Radix Polygoni Multiflori (Heshouwu)-a single herb, were analyzed by network pharmacology study. Based on the network pharmacology framework, we exploited the potential HILI effects of XCHT and Heshouwu by predicting the molecular mechanisms of HILI and identified the potential hepatotoxic ingredients in XCHT and Heshouwu. According to our network results, kaempferol and thymol in XCHT and rhein in Heshouwu exhibit the largest number of liver injury target connections, whereby CASP3, PPARG and MCL1 may be potential liver injury targets for these herbal medicines. This network pharmacology assay might serve as a useful tool to explore the underlying molecular mechanism of HILI. Based on the theoretical predictions, further experimental verification should be performed to validate the accuracy of the predicted interactions between herbal ingredients and protein targets in the future. VSports手机版.
Keywords: Herb-Induced Liver Injury; Radix Polygoni Multiflori; Xiao-Chai-Hu-Tang; hepatoprotective Chinese herbal medicines; network pharmacology. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare Jno conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Liao Y.H., Lin C.C., Lai H.C., Chiang J.H., Lin J.G., Li T.C. Adjunctive traditional Chinese medicine therapy improves survival of liver cancer patients. Liver Int. 2015;35:2595–2602. doi: 10.1111/liv.12847. - VSports在线直播 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amagaya S., Hayakawa M., Ogihara Y., Ohta Y., Fujiwara K., Oka H., Oshio H., Kishi T. Treatment of chronic liver injury in mice by oral administration of xiao-chai-hu-tang. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1989;25:181–187. - VSports注册入口 - PubMed
-
- Tajiri H., Kozaiwa K., Ozaki Y., Miki K., Shimuzu K., Okada S. Effect of sho-saiko-to(xiao-chai-hu-tang) on HBeAg clearance in children with chronic hepatitis B virus infection and with sustained liver disease. Am. J. Chin. Med. 1991;19:121–129. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X91000193. - DOI (V体育ios版) - PubMed
-
- Deng G., Kurtz R.C., Vickers A., Lau N., Yeung K.S., Shia J., Cassileth B. A single arm phase II study of a Far-Eastern traditional herbal formulation (sho-sai-ko-to or xiao-chai-hu-tang) in chronic hepatitis C patients. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011;136:83–87. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.04.008. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
Substances
- V体育官网 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

