Human mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase assembly factor COX18 acts transiently as a membrane insertase within the subunit 2 maturation module
- PMID: 28330871
- PMCID: PMC5427259 (VSports在线直播)
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.778514
"V体育平台登录" Human mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase assembly factor COX18 acts transiently as a membrane insertase within the subunit 2 maturation module
VSports最新版本 - Abstract
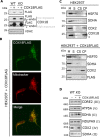
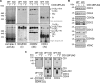
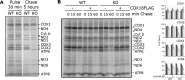
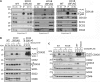
Defects in mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase or respiratory chain complex IV (CIV) assembly are a frequent cause of human mitochondrial disorders. Specifically, mutations in four conserved assembly factors impinging the biogenesis of the mitochondrion-encoded catalytic core subunit 2 (COX2) result in myopathies VSports手机版. These factors afford stability of newly synthesized COX2 (the dystonia-ataxia syndrome protein COX20), a protein with two transmembrane domains, and maturation of its copper center, CuA (cardiomyopathy proteins SCO1, SCO2, and COA6). COX18 is an additional COX2 assembly factor that belongs to the Oxa1 family of membrane protein insertases. Here, we used a gene-editing approach to generate a human COX18 knock-out HEK293T cell line that displays isolated complete CIV deficiency. We demonstrate that COX20 stabilizes COX2 during insertion of its N-proximal transmembrane domain, and subsequently, COX18 transiently interacts with COX2 to promote translocation across the inner membrane of the COX2 C-tail that contains the apo-CuA site. The release of COX18 from this complex coincides with the binding of the SCO1-SCO2-COA6 copper metallation module to COX2-COX20 to finalize COX2 biogenesis. Therefore, COX18 is a new candidate when screening for mitochondrial disorders associated with isolated CIV deficiency. .
Keywords: COX18; COX2; COX20; SCO1; SCO2; cardiomyopathy; cytochrome c oxidase (complex IV); mitochondrial metabolism; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex; transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN) V体育安卓版. .
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. V体育ios版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
"V体育官网" Figures



References (V体育ios版)
-
- Fontanesi F., and Barrientos A. (2013) Mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase assembly in health and in human diseases, in Mitochondrial Disorders Caused by Nuclear Genes. Part 3 (Wong L. E., ed) pp. 239–259, Springer Science, New York
-
- Nijtmans L. G., Taanman J. W., Muijsers A. O., Speijer D., and Van den Bogert C. (1998) Assembly of cytochrome-c oxidase in cultured human cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 254, 389–394 - PubMed
MeSH terms
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
Substances
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

