Comparison of Collection Methods for Fecal Samples in Microbiome Studies
- PMID: 27986704
- PMCID: V体育官网 - PMC5253972
- DOI: V体育平台登录 - 10.1093/aje/kww177
Comparison of Collection Methods for Fecal Samples in Microbiome Studies (VSports手机版)
Abstract
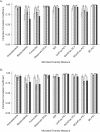
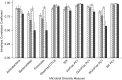
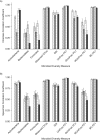
Prospective cohort studies are needed to assess the relationship between the fecal microbiome and human health and disease. To evaluate fecal collection methods, we determined technical reproducibility, stability at ambient temperature, and accuracy of 5 fecal collection methods (no additive, 95% ethanol, RNAlater Stabilization Solution, fecal occult blood test cards, and fecal immunochemical test tubes). Fifty-two healthy volunteers provided fecal samples at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, in 2014. One set from each sample collection method was frozen immediately, and a second set was incubated at room temperature for 96 hours and then frozen. Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) were calculated for the relative abundance of 3 phyla, 2 alpha diversity metrics, and 4 beta diversity metrics. Technical reproducibility was high, with ICCs for duplicate fecal samples between 0. 64 and 1. 00 VSports手机版. Stability for most methods was generally high, although the ICCs were below 0. 60 for 95% ethanol in metrics that were more sensitive to relative abundance. When compared with fecal samples that were frozen immediately, the ICCs were below 0. 60 for the metrics that were sensitive to relative abundance; however, the remaining 2 alpha diversity and 3 beta diversity metrics were all relatively accurate, with ICCs above 0. 60. In conclusion, all fecal sample collection methods appear relatively reproducible, stable, and accurate. Future studies could use these collection methods for microbiome analyses. .
Keywords: feces; microbiota; specimen collection V体育安卓版. .
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health 2016. This work is written by (a) US Government employee(s) and is in the public domain in the US V体育ios版. .
Figures
References
-
- Ley RE. Obesity and the human microbiome. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2010;26(1):5–11. - PubMed
-
- Vogtmann E, Goedert JJ. Epidemiologic studies of the human microbiome and cancer. Br J Cancer. 2016;114(3):237–242. - "V体育官网入口" PMC - PubMed
-
- Feng Q, Liang S, Jia H, et al. Gut microbiome development along the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6528. - PubMed
-
- Weir TL, Manter DK, Sheflin AM, et al. Stool microbiome and metabolome differences between colorectal cancer patients and healthy adults. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e70803. - V体育安卓版 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
MeSH terms
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
Grants and funding (VSports在线直播)
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases (V体育ios版)

