Hepatitis C Virus Infection of Cultured Human Hepatoma Cells Causes Apoptosis and Pyroptosis in Both Infected and Bystander Cells
- PMID: 27974850
- PMCID: PMC5156923
- DOI: 10.1038/srep37433
Hepatitis C Virus Infection of Cultured Human Hepatoma Cells Causes Apoptosis and Pyroptosis in Both Infected and Bystander Cells
Abstract
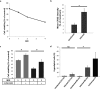
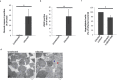
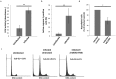
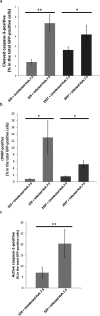
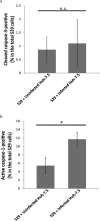
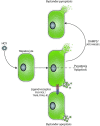
Individuals infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) are at high risk of developing progressive liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). How HCV infection causes liver destruction has been of significant interest for many years, and apoptosis has been proposed as one operative mechanism. In this study, we employed a tissue culture-adapted strain of HCV (JFH1T) to test effects of HCV infection on induction of programmed cell death (PCD) in Huh-7. 5 cells. We found that HCV infection reduced the proliferation rate and induced caspase-3-mediated apoptosis in the infected cell population. However, in addition to apoptosis, we also observed infected cells undergoing caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis, which was induced by NLRP3 inflammasome activation. By co-culturing HCV-infected Huh-7. 5 cells with an HCV-non-permissive cell line, we also demonstrated induction of both apoptosis and pyroptosis in uninfected cells VSports手机版. Bystander apoptosis, but not bystander pyroptosis, required cell-cell contact between infected and bystander cells. In summary, these findings provide new information on mechanisms of cell death in response to HCV infection. The observation that both apoptosis and pyroptosis can be induced in bystander cells extends our understanding of HCV-induced pathogenesis in the liver. .
Figures (VSports注册入口)
References
-
- Freeman A. J. et al.. Estimating progression to cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 34, 809–816, doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.27831 (2001). - "VSports最新版本" DOI - PubMed
-
- Marcellin P. Hepatitis C: the clinical spectrum of the disease. Journal of hepatology 31 Suppl 1, 9–16 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Elmore S. Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicologic pathology 35, 495–516, doi: 10.1080/01926230701320337 (2007). - VSports在线直播 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育2025版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Substances
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
LinkOut - more resources (VSports注册入口)
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

