VSports - Emerging therapeutic agents for lung cancer
- PMID: 27938382
- PMCID: PMC5148871
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-016-0365-z
Emerging therapeutic agents for lung cancer
Abstract
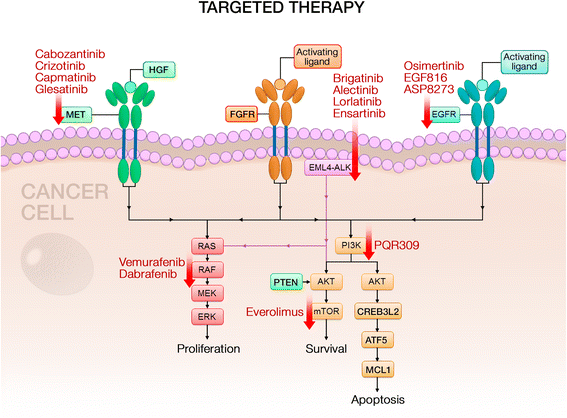
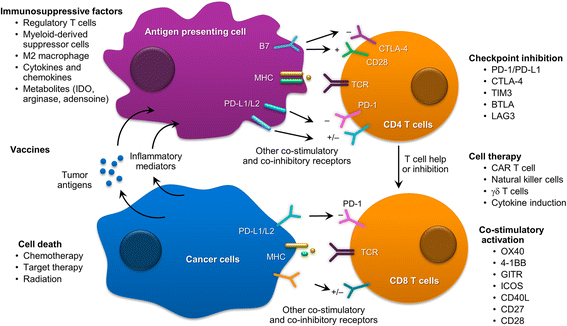
Lung cancer continues to be the most common cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Recent advances in molecular diagnostics and immunotherapeutics have propelled the rapid development of novel treatment agents across all cancer subtypes, including lung cancer. Additionally, more pharmaceutical therapies for lung cancer have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in the last 5 years than in previous two decades. These drugs have ushered in a new era of lung cancer managements that have promising efficacy and safety and also provide treatment opportunities to patients who otherwise would have no conventional chemotherapy available. In this review, we summarize recent advances in lung cancer therapeutics with a specific focus on first in-human or early-phase I/II clinical trials. These drugs either offer better alternatives to drugs in their class or are a completely new class of drugs with novel mechanisms of action VSports手机版. We have divided our discussion into targeted agents, immunotherapies, and antibody drug conjugates for small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We briefly review the emerging agents and ongoing clinical studies. We have attempted to provide the most current review on emerging therapeutic agents on horizon for lung cancer. .
Keywords: Immunotherapy; Lung cancer; Phase I/II clinical trial; Targeted agents. V体育安卓版.
Figures (V体育安卓版)
References
-
- Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, Giroux DJ, Groome PA, Rami-Porta R, Postmus PE, Rusch V, Sobin L, Committee IAftSoLCIS, Institutions P The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2(8):706–714. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31812f3c1a. - DOI (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
-
- Smith AD, Roda D, Yap TA. Strategies for modern biomarker and drug development in oncology. J Hematol Oncol. 2014;7:70. doi: 10.1186/s13045-014-0070-8. - "V体育ios版" DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, Lu S, Zhang L, Hu C, Luo Y, Chen L, Ye M, Huang J, Zhi X, Zhang Y, Xiu Q, Ma J, You C. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(8):735–742. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70184-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, Seto T, Crino L, Ahn MJ, De Pas T, Besse B, Solomon BJ, Blackhall F, Wu YL, Thomas M, O’Byrne KJ, Moro-Sibilot D, Camidge DR, Mok T, Hirsh V, Riely GJ, Iyer S, Tassell V, Polli A, Wilner KD, Janne PA. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(25):2385–2394. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1214886. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sun W, Yuan X, Tian Y, Wu H, Xu H, Hu G, Wu K. Non-invasive approaches to monitor EGFR-TKI treatment in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:95. doi: 10.1186/s13045-015-0193-6. - DOI (V体育ios版) - PMC - PubMed
V体育官网入口 - Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Substances
- VSports手机版 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources (V体育官网入口)
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (V体育官网)
"VSports注册入口" Medical

